The 10 Biggest Crypto Hacks in History
This article takes an in-depth look at the 10 most shocking crypto hack incidents in history. We will explore famous hacker groups, common attack methods, and the sophisticated money-laundering techniques used in the crypto world. We will also compare traditional hacking and crypto hacking, while providing valuable security tips to help investors avoid potential risks.
Overview
The rise of cryptocurrencies brought immense wealth and technological innovation, but it also introduced serious security risks. Hacking attacks have caused billions of dollars in losses over the past decade, remaining one of the crypto industry’s biggest vulnerabilities.
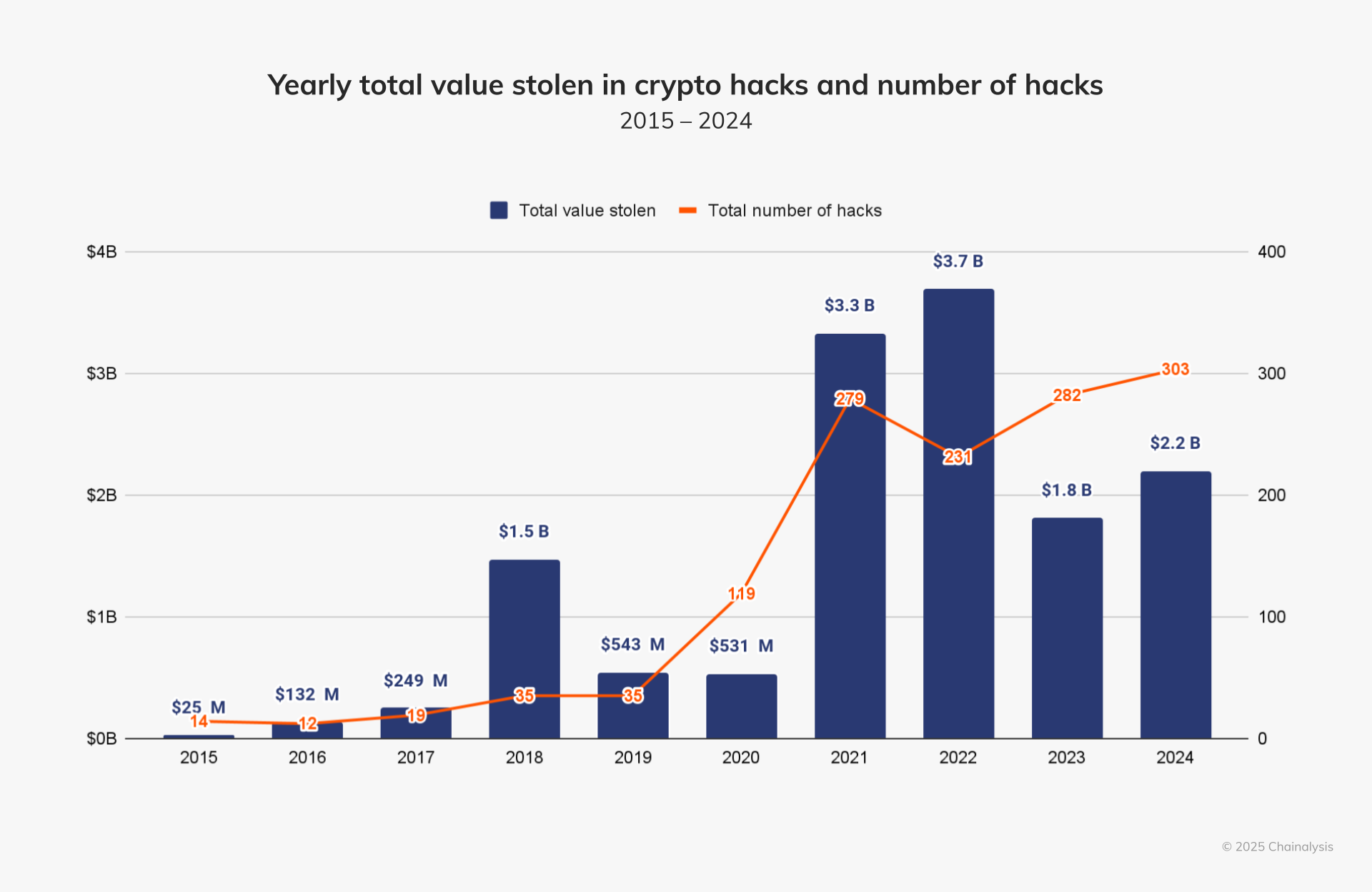
In 2024, crypto platforms lost a total of $2.2 billion — a 21.07% increase compared to the previous year. The attacks were particularly concentrated between January and July. During this period, North Korea–linked cybercriminals stole $1.34 billion, accounting for 61% of total losses.
Below is a list of the most impactful and destructive 10 hacks in crypto history. Each not only caused massive financial losses but also led to a complete reshaping of security measures across the industry.
Source: https://www.chainalysis.com/blog/kripto-hacking-stolen-funds-2025/
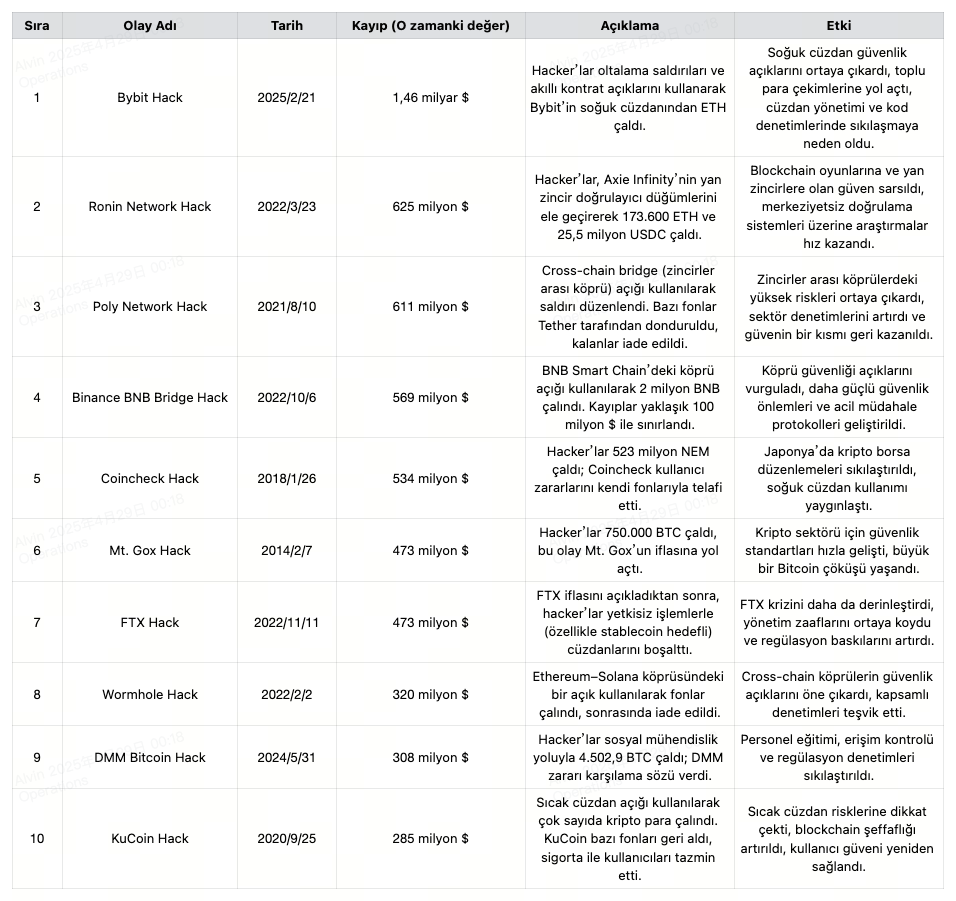
The 10 Biggest Crypto Hacks in History
The global crypto sector has been shaken by numerous major hacks that have collectively caused billions in losses. The largest crypto attack occurred during the Bybit hack in February 2025. Hackers exploited sophisticated phishing attacks and smart contract vulnerabilities to steal large amounts of ETH from cold wallets.
The second-largest attack was the Ronin Network hack in March 2022. Validators on Axie Infinity’s sidechain were compromised, resulting in the theft of $625 million worth of ETH and USDC.
Other notable attacks include:
- Poly Network (2021): $611 million stolen by exploiting a cross-chain bridge vulnerability.
- Binance BNB Bridge Hack (2022): $569 million loss.
- Coincheck (2018): $534 million stolen after the exchange was hacked.
- Mt. Gox (2014): $473 million lost after the exchange collapsed.
In addition, platforms like FTX, Wormhole, DMM Bitcoin, and KuCoin were also hit by large-scale attacks. Although some losses were partially covered by insurance or compensation programs, these incidents highlight that serious security vulnerabilities still exist within the crypto industry.

Source: https://cointelegraph.com/news/kucoin-ceo-says-insurance-covered-16-of-losses-from-285m-hack-in-2020
Impact and Future Outlook
General Trends and Key Security Issues in the Industry
- Cross-Chain Bridges: High-Risk Targets
Cross-chain bridges have become attractive targets for hackers due to their structural complexity and their role in facilitating large-volume asset transfers. The need for simultaneous transaction and security synchronization between multiple blockchains significantly increases the risk of vulnerabilities.
Numerous large-scale attacks on bridge protocols demonstrate that this infrastructure’s security is still far from perfect. Therefore, tightening security audits, designing stronger protocols, and developing inter-chain standards will be crucial in the future.
Notable Cross-Chain Bridge Attacks:
- Poly Network (2021): $613 million stolen. The attack exposed vulnerabilities in cross-chain smart contracts.
- Binance BNB Bridge (2022): $570 million lost due to exploitation of a validation vulnerability.
- Wormhole (2022): $326 million stolen due to a flaw in the smart contract validation mechanism.
Impact on the Industry:
These attacks revealed how vulnerable cross-chain infrastructures are. As a result:
- There has been a growing shift toward technologies such as multi-signature systems and Multi-Party Computation (MPC) to enhance security.
- Instead of traditional bridge solutions, Rollups and native interoperability protocols (such as LayerZero) are becoming increasingly adopted.
This transition aims to ensure lower attack surfaces and higher security in cross-chain interactions.
Source: https://www.halborn.com/blog/post/anlatildi-wormhole-hack-subat-2022
- Weaknesses in Cold/Hot Wallet Management
Wallet management is one of the most critical aspects of crypto security. Even cold wallets, which are generally considered safer, can be targeted through social engineering, fraud, or insider access vulnerabilities. Hot wallets, being constantly connected to the internet, fall into the highest-risk category.
Big Events:- Bybit (2025): A wallet management breach occurred, with an estimated loss of around $1.4 billion.
- Coincheck (2018): $534 million worth of NEM stolen. The hot wallet lacked multi-signature protection.
- KuCoin (2020): Hackers accessed private keys and stole assets worth $280 million.
Impact on the Industry:
- Cold wallet usage is being expanded, while multi-signature verification and Hardware Security Modules (HSM) are becoming standard practice.
- Transparency tools such as Proof of Reserves (PoR) are increasingly adopted to reduce the risks of centralized wallet management.
These developments are seen as critical steps toward enhancing asset security and reinforcing user confidence.

Source: https://www.ic3.gov/PSA/2025/PSA250226
- Weaknesses in Side Chains and Emerging Technologies
Side chains remain vulnerable to attacks, especially in structures with weak authenticator security. The Ronin Network attack (2022) was one of the most striking examples of this risk. Many blockchain games and GameFi applications operate with low levels of decentralization, making them a target for hackers.
Big Event:- Ronin Network (2022): Hackers gained control of 5 out of 9 validator nodes, stealing $620 million worth of ETH and USDC. This attack exposed significant security flaws in game-oriented blockchain networks.
Impact on the Industry:
- Projects began decentralizing their validator networks to improve security. The number of nodes is being increased, and stronger consensus mechanisms are being implemented.
- GameFi and NFT-focused sidechain projects are migrating to more secure Layer 2 solutions. Rollup infrastructures like Arbitrum and Optimism are standing out during this transition.
This shift aims to create a more balanced architecture in terms of both performance and security.

Source: https://www.technologyreview.com/2022/04/15/1050259/a-620-million-hack-just-another-day-in-crypto/
- Systemic Risks in Centralized Exchanges (CEXs)
Centralized exchanges (CEXs) are inherently centralized in structure, which makes them vulnerable to various risks such as management errors, internal fraud, and external attacks. Systemic failures and security loopholes have resulted in large-scale losses of user funds.
Big Events:- Mt. Gox (2014): 850,000 BTC stolen (worth roughly $4.7 billion today). The incident deeply shook the crypto market.
- FTX (2022): $8 billion in customer funds lost due to internal misconduct — one of the most significant trust failures in crypto history.
- DMM Bitcoin (2024): A large-scale hack exposed critical weaknesses in the platform’s security protocols.
Impact on the Industry:
- Centralized exchanges are now subject to regulatory measures such as Proof of Reserves (PoR) and asset segregation policies.
- Users are shifting toward decentralized exchanges (DEXs), where they retain control of their assets. This has also increased demand for customizable and self-custody wallets.
These developments are accelerating the industry’s shift toward more transparent and user-centered solutions to counter trust issues in centralized structures.
These incidents have made the crypto industry place far greater emphasis on security.
From a technical perspective, the industry has begun investing heavily in areas such as wallet management, smart contract auditing, and cross-chain bridge security design.
At the management level, centralized platforms have been forced to strengthen internal access controls and expand staff training.
However, despite all these efforts, security challenges—especially in an environment where technology evolves rapidly—remain one of the key obstacles to the sustainable growth of the crypto industry.
Regulatory Trends and the Acceleration of Compliance
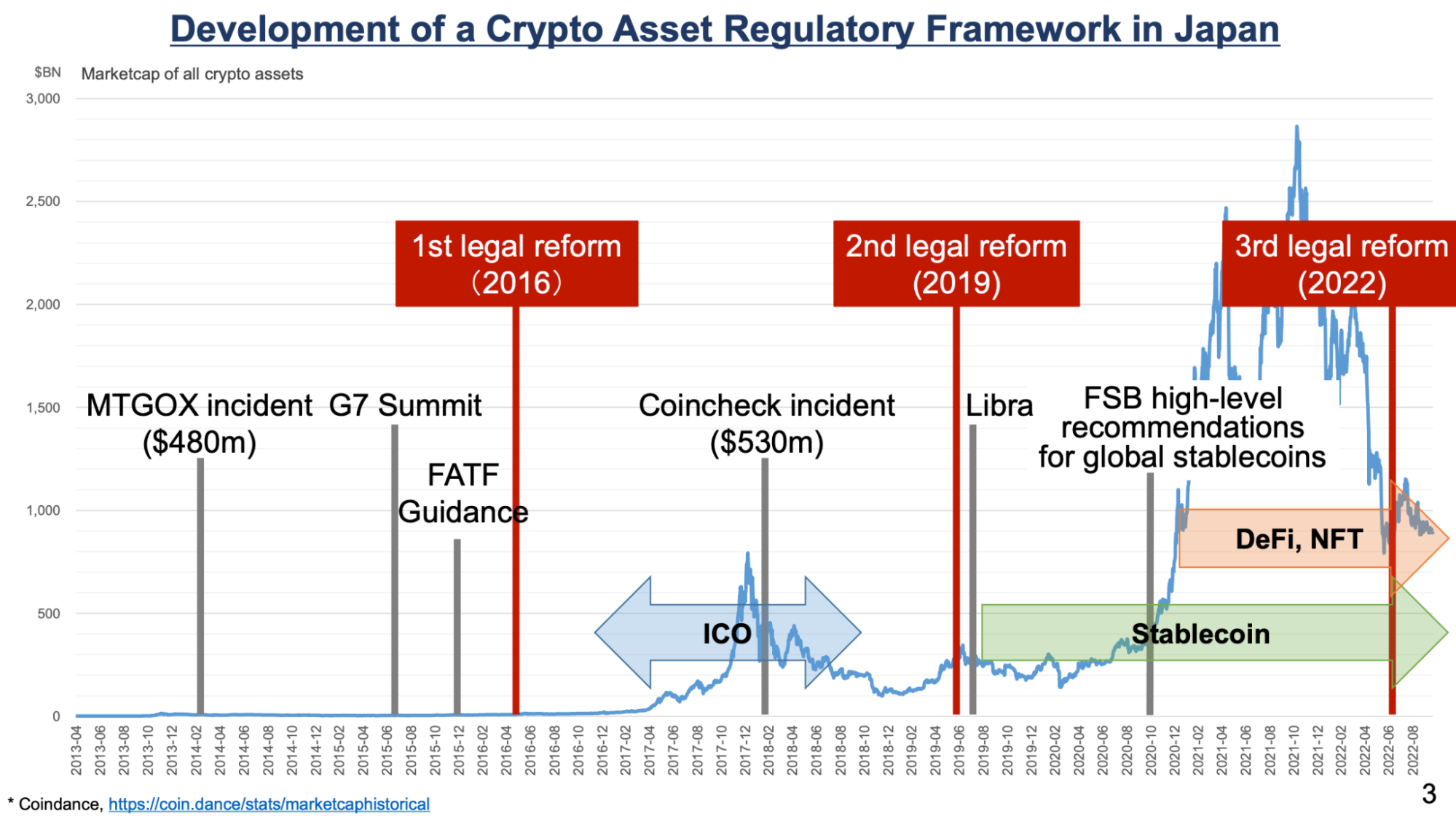
High-profile hacks—particularly large-scale incidents like Mt. Gox and FTX that caused massive financial losses and systemic impacts—have led to a sharp rise in regulatory oversight of the crypto sector. These developments have made global regulatory approaches more structured and interventionist.
From Regulatory Gaps to Structured Oversight
During the Mt. Gox hack in 2014, there was virtually no regulatory framework in the crypto markets. This made it difficult for investors to recover their losses and caused a major confidence crisis in the industry. In the 2020s, the regulatory gaps began to close rapidly. Japan tightened licensing, custody, and auditing requirements following the Coincheck hack. The European Union established a comprehensive crypto regulatory framework across the EU with MiCA (Markets in Crypto Assets). The United States, after the FTX collapse, took tougher actions against crypto platforms through the SEC.
These new regulations mandate requirements such as KYC/AML compliance, asset segregation, regular audits, and transparency reporting for crypto exchanges and service providers.
Source: https://www.fsa.go.jp/en/news/2022/20221207/01.pdf
Regulating Cross-Chain Bridges and DeFi
Hacks such as Poly Network and Wormhole exposed regulatory blind spots in the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem. In the future, regulators may attempt to monitor DeFi protocols via on-chain tracking technologies or require protocol developers to disclose their identities. However, care must be taken to ensure that innovation is not stifled during this process.
Stricter Cold/Hot Wallet Management Standards
Attacks on platforms such as Bybit (2025) and KuCoin (2020) have prompted regulators to focus more on exchange wallet security. Future regulations may include mandatory use of cold wallets and the requirement for exchanges to regularly publish public Proof of Reserves.
Impact:
Stronger regulations may increase compliance costs in the short term, especially for smaller exchanges. However, these measures will promote standardization across the industry and help reduce systemic risks in the long term. Japan encouraged widespread use of cold wallets through the regulations it implemented following the Coincheck attack. The collapse of FTX led to a rapid global surge in demand for exchange transparency.
The Path to Rebuilding Industry Trust
Crypto hacks — especially major incidents like Mt. Gox and FTX — severely damaged investor confidence after massive user losses. Rebuilding trust requires improvements in both technology and institutional safeguards.
Enhancing Technical Transparency
Incidents like KuCoin (2020) and Wormhole (2022) have shown that blockchain transparency can aid in tracing and recovering some stolen funds through on-chain tracking and protocol fixes. In the future, Proof of Reserves (PoR) could become an industry standard, requiring centralized platforms to regularly disclose their asset reserves and thereby increase user confidence.
Crypto hacks, particularly large-scale events such as Mt. Gox and FTX, have seriously shaken investor confidence due to massive user losses. Rebuilding this confidence requires strengthening both technological infrastructure and institutional practices.
Cases like KuCoin (2020) and Wormhole (2022) revealed how blockchain transparency can effectively track and sometimes recover stolen funds. These incidents made the need for transparency at the technical level more apparent. In the future, Proof of Reserves (PoR) practices could become a standard, requiring centralized platforms to regularly disclose asset reserves and strengthen user trust.
Compensation and Insurance Mechanisms
Coincheck (2018) and DMM Bitcoin (2024) partially restored confidence by compensating users through company funds or insurance after major hacking incidents. Such practices indicate that more systematic solutions may emerge in the crypto sector in the future. The establishment of an industry-wide insurance fund or mandatory compensation mechanisms could strengthen user protection. As in traditional finance, a type of deposit insurance model could gradually be integrated into crypto markets. This approach could play a critical role in rebuilding trust, particularly for small investors.

Source: relminsurance.com
The Growing Trend of Decentralization
After the 2022 attack on the Ronin Network, the industry began re-evaluating the importance of decentralized validation mechanisms.With the rise of decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and self-custody wallets, users have started reducing their reliance on centralized platforms to spread their risks.
Rebuilding trust is a long-term process. In the short term, investors tend to move toward large, regulated exchanges or fully decentralized solutions.However, in the long run, if the industry can effectively leverage technological innovation and self-regulation to reduce the frequency and impact of hacks, the trust crisis may gradually ease. This could lead to the formation of a more sustainable market structure.
Famous Crypto Hacker Groups
Hacking incidents in the cryptocurrency field are often carried out by cybercriminal groups equipped not only with technical expertise but also with advanced tactics based on social engineering, phishing, and protocol exploitation. These groups have caused millions of dollars in losses by targeting vulnerabilities in blockchain infrastructure.
Below are brief profiles of some hacker groups that have gained notoriety in the crypto industry. This information is compiled from public reports and historical incidents. However, the identities and state affiliations of these groups are often unverifiable, so some details may be speculative.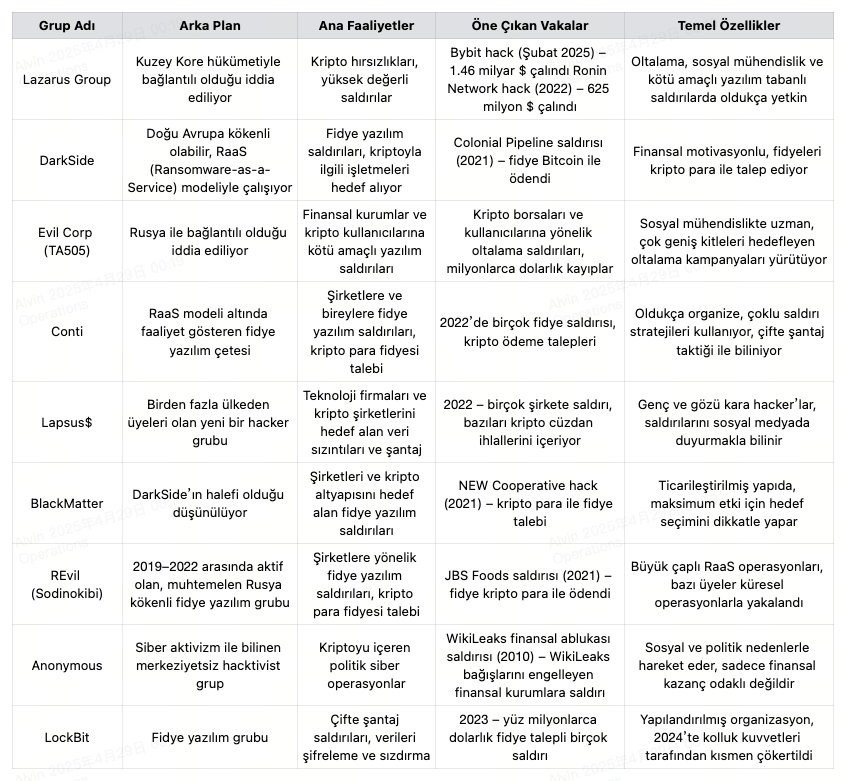
Different hacker groups harm the crypto industry through different methods. Some, like the Lazarus Group, focus directly on stealing crypto assets; while others, such as DarkSide and REvil, lock systems with ransomware attacks and demand cryptocurrency in exchange for decryption. The identities and affiliations of these groups are typically based on public reports, official statements, and cybersecurity analyses. However, this information is not always conclusive, and some attributions remain disputed. Crypto hacking groups generally operate in deep secrecy. This makes it difficult to track and hold them accountable both technically and legally. It can also give certain incidents political dimensions.
In a rapidly evolving technological landscape, the emergence of new and more sophisticated groups is inevitable. This demonstrates that crypto security is not merely a technical issue but a dynamic field that requires continuous threat assessment and compliance adaptation.

Source: channelfutures.com
Cyber Attacks and Defense Measures
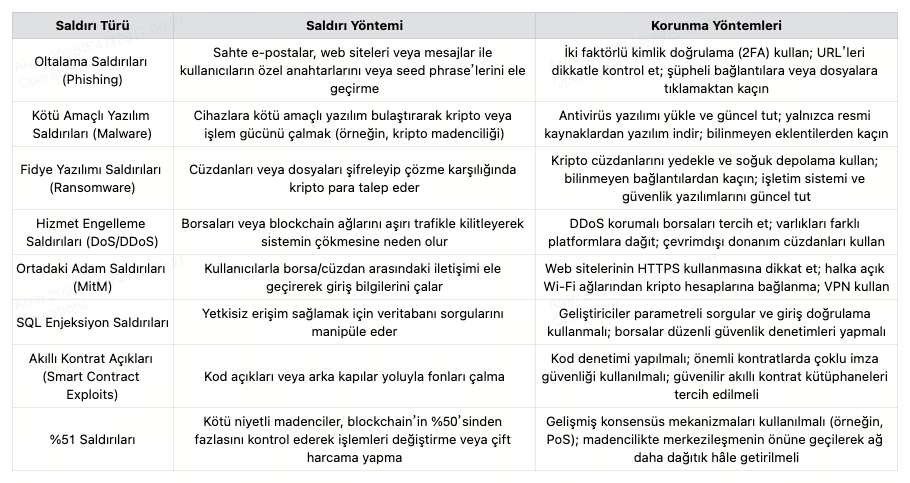
Cyberattacks in the crypto industry can be carried out using various techniques. Hackers target systems through methods such as phishing, malware, ransomware, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, SQL injections, smart contract vulnerabilities, and 51% attacks. Each of these attacks can lead to severe financial losses or systemic disruptions.
In contrast, several defense measures play a crucial role in mitigating these risks. Two-factor authentication (2FA), antivirus software, regular wallet backups, encrypted network infrastructures, and periodic security audits all help protect users and platforms. An effective security approach is fundamental to addressing these threats at both individual and institutional levels.
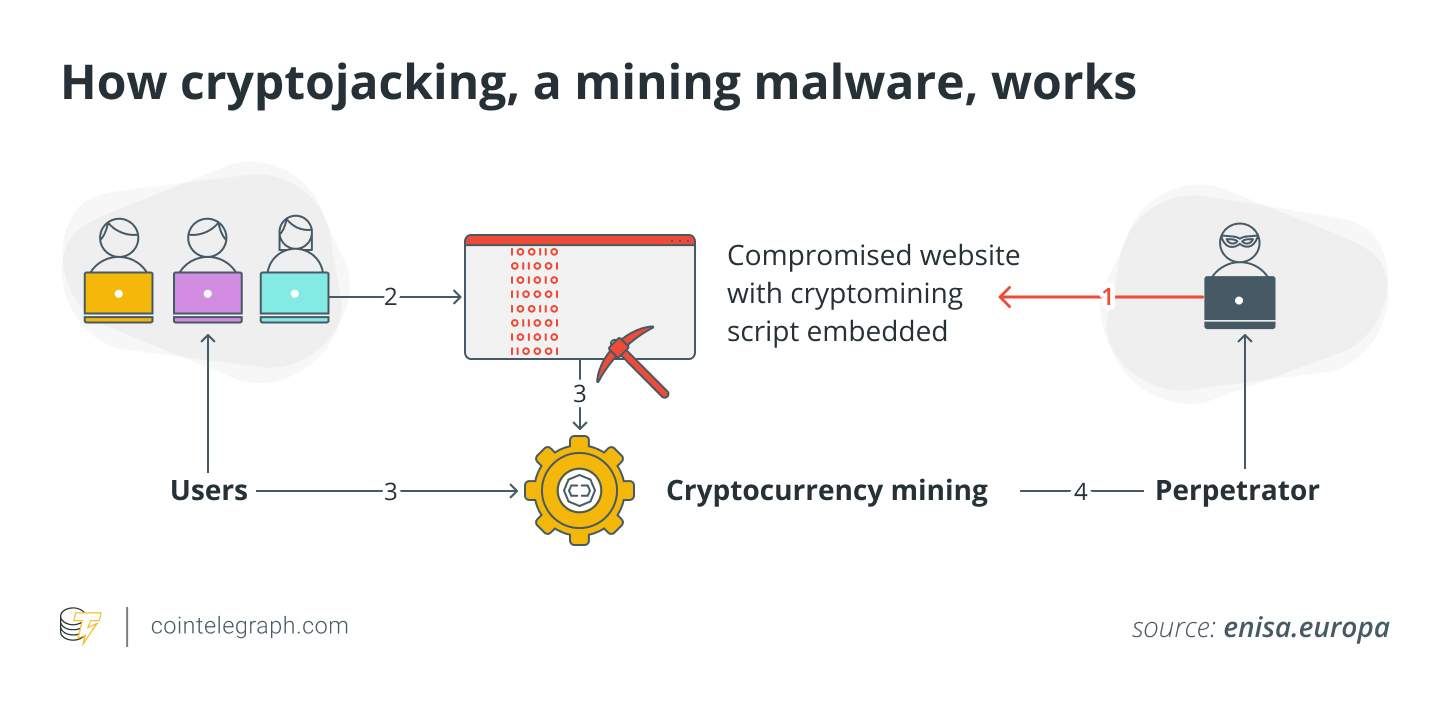
Source: cointelegraph.com
Money Laundering Methods and Prevention Measures
Money laundering activities in the crypto world are increasingly carried out with more sophisticated methods. Common techniques include mixers, cross-chain bridges, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), over-the-counter (OTC) trades, batch transactions, and exchange-splitting strategies. These methods make tracing difficult and allow illicit funds to appear legitimate.
Various measures can be implemented to prevent these activities. Detecting suspicious transactions across multiple wallet addresses, regularly reviewing transaction histories, and auditing cross-chain bridge security are primary steps. Additionally, choosing only reputable DEX platforms, verifying counterparties in OTC trades, monitoring unusual batched transactions, and controlling inter-exchange fund flows in line with regulations are important.
These measures should be adopted by both users and platforms to prevent money laundering and build a transparent crypto ecosystem.
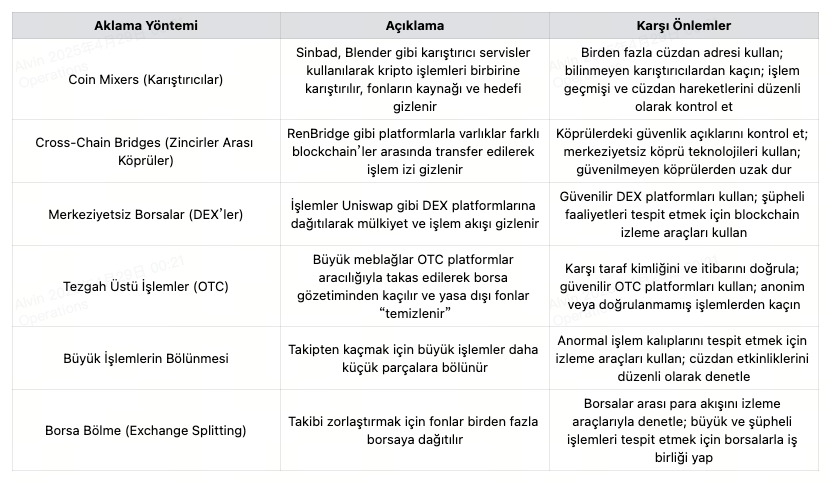
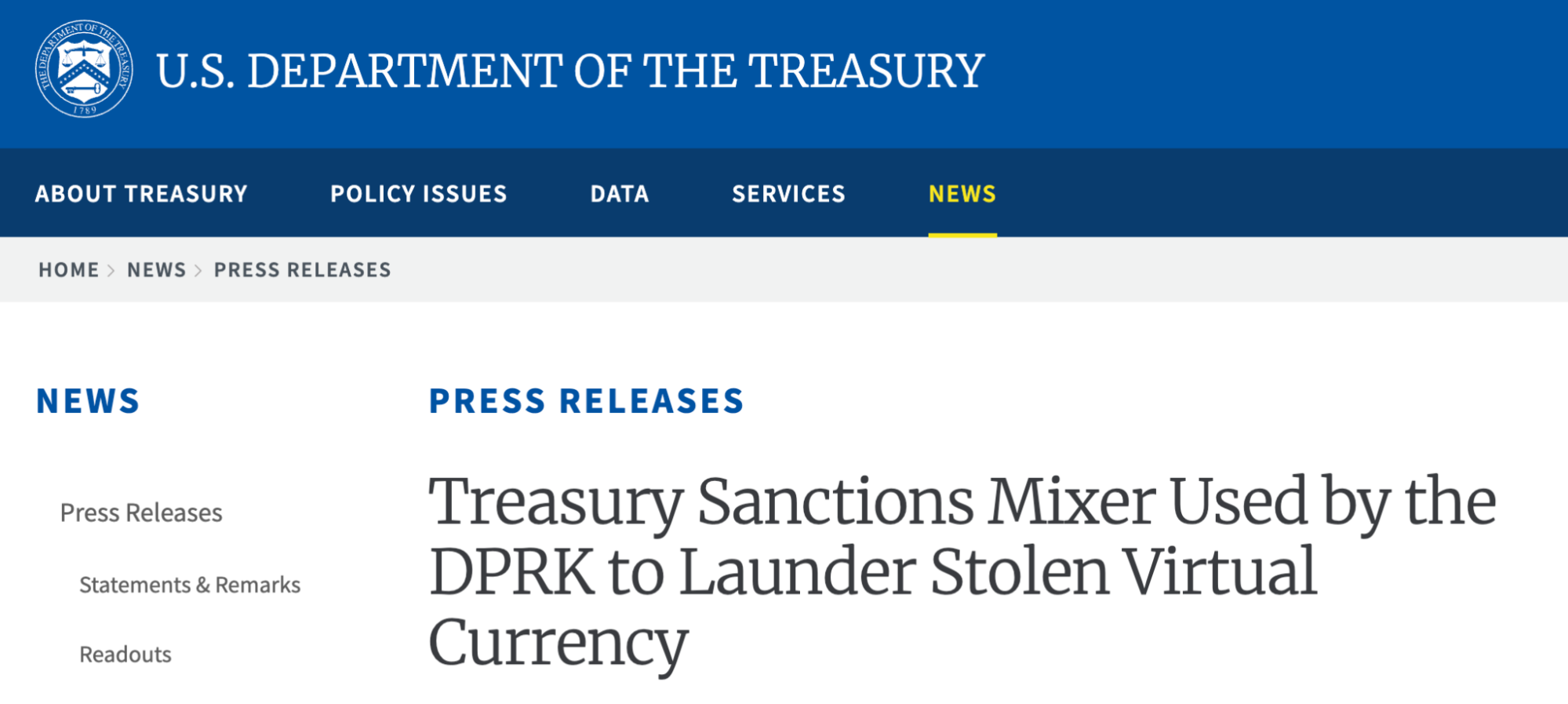
Source: home.treasury.gov
Comparison Between Crypto Hackers and Traditional Hackers
Crypto hacks and traditional cyberattacks differ significantly in their methods, target systems, and impacts. Crypto hackers focus on exploiting vulnerabilities in blockchain infrastructure, smart contracts, and decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols. Their objectives are typically to seize digital assets directly or to manipulate on-chain systems.
Traditional hackers, by contrast, often target corporate IT infrastructures, network security, and user devices. Those attacks can result in data breaches, system outages, or ransom demands.
As cryptocurrencies become more widespread, the complexity of such attacks is increasing as well. Therefore, improving security measures, strengthening regulatory frameworks, and raising user awareness will be the most critical factors determining defense capacity against both crypto and traditional attacks.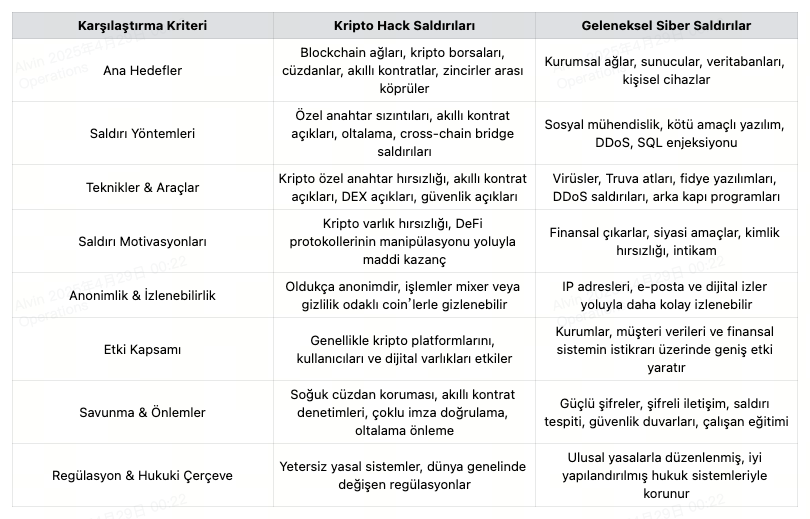
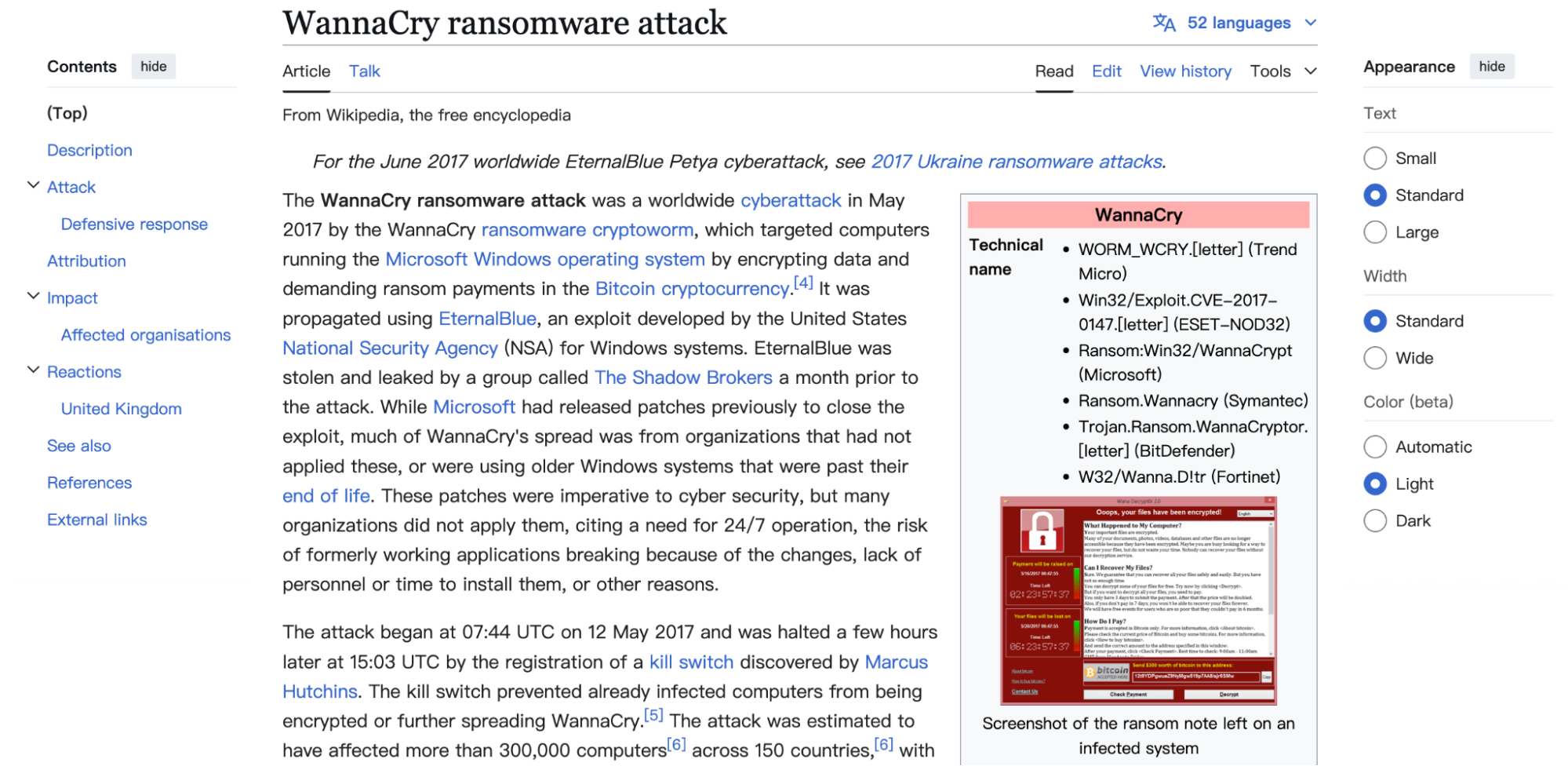
Source: https://tr.wikipedia.org/wiki/WannaCry_fidye_uygulama_saldirisi
Investment Tips for Individual Investors
Reduce Risk by Diversifying Investments
Hacks have clearly shown that a security breach on a single platform or project can put an entire investment at risk. Therefore, spreading funds across multiple platforms and projects reduces the impact of a single incident on an investment portfolio. Diversification balances investor risk against natural volatility and security threats in crypto markets.
Choose Secure Platforms
Using platforms with robust security infrastructure is critical to reducing risk. Prefer exchanges that offer cold wallet support (offline asset storage), two-factor authentication (2FA), multi-signature wallet structures, and asset insurance.
Investors should carefully examine what measures a platform has taken to protect user funds. Such measures include insurance funds like SAFU, regular reserve disclosures, and the platform’s financial soundness.
Understanding and Using Risk Management Tools
It is important to leverage exchange-offered insurance funds and asset monitoring technologies to enhance security in crypto investments. Platforms that can respond quickly to hacks and have asset-recovery capabilities are safer choices for investors.
At the same time, there are basic precautions individual users can take. Always enable two-factor authentication (2FA). Regularly check account activity and review your transaction history to detect unusual movements. Quick detection of suspicious activity plays a critical role in preventing potential threats.
Risk management is not just an option; it is a necessity for long-term secure investing.
Source: play.google.com/store
Maintain a Long-Term Investment Perspective
Short-term volatility in crypto markets is inevitable. However, the industry’s security measures and technological infrastructure are improving over time. Investing in projects that learn from past attacks and strengthen their systems can yield more stable returns in the long run.
Be Careful of Phishing Attacks and Social Engineering
Hackers are increasingly using more advanced social-engineering tactics. Phishing attacks, in particular, remain one of the most common methods for stealing user credentials. Investors should avoid suspicious links, never share personal credentials, and cultivate basic security awareness.
Do Research Before Investing
Before investing in a project, carefully review its history, technical architecture, team, and implement security measures. Rather than blindly following market trends, favor projects with solid fundamentals and proven security.
Stay Updated, Stay Informed
The crypto industry evolves rapidly. Security protocols, regulations, and technological developments are constantly being updated. Therefore, it is crucial for investors to closely follow developments and make informed, timely decisions.
General Advice
Individual investors should increase security awareness, be meticulous when choosing platforms, and diversify their investments. They should use risk-management tools effectively to reduce single-point dependency and adopt a long-term perspective. In this way, by focusing on projects that continuously improve defenses and resist security challenges, they can build a more robust investment strategy.
Conclusion
While the rapid rise of the crypto industry brings major innovation and economic opportunities, security remains one of the most critical challenges. Large-scale hacks over the years have caused billions in losses and exposed structural security weaknesses in exchanges, wallet systems, and cross-chain infrastructures.
As hack techniques become more sophisticated—and often involve organized crime—increasing security measures and strengthening regulatory frameworks have become an unavoidable priority for the industry’s sustainable growth.
Despite all these challenges, the industry is taking determined steps to enhance security through technological advancements and preventive mechanisms. Measures such as smart contract audits, decentralized security solutions, and cybersecurity training for employees aim to reduce risks and restore user confidence.
Looking ahead, as technology matures and regulations become clearer and more inclusive, the crypto market is expected to become safer, more stable, and more widely adopted. However, achieving this goal will require collective efforts not only from individual investors but also from developers, platforms, regulators, and all industry stakeholders. Only with this collective awareness can effective defenses be built against hacking, money laundering can be combated, and the crypto market can grow healthily.
Related Articles

Spot Crypto ETFs: Global Rise and Turkey’s Roadmap

November 2025 Crypto Summary: Institutional Adoption and Market Dynamics