Bitcoin Nedir?
Bitcoin nedir?
Bitcoin, kullanıcıların herhangi bir aracı olmadan doğrudan işlem yapmasını sağlayan merkeziyetsiz bir dijital para birimidir. Bitcoin’in temelleri, Satoshi Nakamoto tarafından Ekim 2008’de yayımlanan Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System adlı makaleye dayanır.
Bitcoin, merkeziyetsiz, güvenli ve kendi kendine işleyen bir elektronik para sistemi olarak yalnızca düğümler oluşturularak, kriptografi ile doğrulanarak ve blockchain adı verilen halka açık dağıtılmış bir deftere kaydedilerek çalışır. Merkezi olmayan dijital para fikri daha önce de ortaya atılmış olsa da, Bitcoin bu kavramı pratikte hayata geçiren ve kripto para endüstrisinin temelini oluşturan ilk sistemdir. On binlerce insanın katılımıyla küresel bir topluluk haline gelmiş ve zamanla birçok platform, cüzdan, borsa, seyahat hizmeti, çevrimiçi ödeme ve oyun gibi gerçek dünyada kullanılabilen uygulamaların ortaya çıkmasını sağlamıştır.
Bitcoin’in güvenliği, sansüre karşı dayanıklılığı, anonimliği ve sınır tanımayan yapısı, onu finansal hizmetlere erişimin kısıtlı olduğu bölgelerde alternatif bir ödeme yöntemi haline getirmiştir. Toplam arzı 21 milyon ile sınırlı olduğundan, zaman içinde değer saklama aracı olarak da görülmeye başlanmış ve kıtlığı nedeniyle “dijital altın” olarak anılmıştır. Bitcoin sahipleri, bu merkeziyetsiz dijital varlığın getirdiği değerle özdeşleşmekte ve uzun vadeli bir yatırım olarak görmektedir.
Dalgalı fiyat hareketlerine rağmen, Bitcoin artık geniş kitleler tarafından tanınmakta ve enflasyona karşı koruma sağlayan merkeziyetsiz bir dijital varlık olarak güçlü bir destekçi topluluğuna sahip olmaya devam etmektedir.
Bitcoin nasıl çalışır?
Bitcoin, sıralı bir işlem zinciri prensibiyle çalışır ve dijital imza ile doğrulanan bir jetonun işlem süreci olarak tanımlanır. Jetonun kendisi, zincir üzerindeki önceki işlemlerden türetilir. Örneğin, A, B’ye bir Bitcoin gönderdiğinde, A’nın bakiyesi -1, B’nin bakiyesi ise +1 olarak güncellenir. Bu sistem, işlemleri kaydederek para biriminin sahipliğini belirleyen şeffaf ve güvenli bir defter yapısı oluşturur.
Tarihteki ilk madeni para olarak bilinen Rai Taşları, önceki sahibinin adının üzeri çizilip yeni sahibinin adının yazılmasıyla mülkiyet değişimini gösteren bir sistemle kullanılıyordu. Bu yöntem, bir defter kaydı mantığıyla işlem geçmişini takip etmeyi sağlıyordu. İşlem kaydı tutma pratiği, günümüzden çok eski zamanlarda kullanılıyordu.
Bitcoin ağında her işlem, tokenların dijital imza ile doğrulanarak defterin güncellenmesiyle gerçekleşir. İşlem sırasında, önceki işlemin referansı ve bir sonraki alıcının ortak anahtarı imzalanarak token yeni sahibine aktarılır. Bu işlem, tüm düğümlere yayınlanan bir bloğa dahil edilir. İşlemin geçerliliği, ağdaki düğümler tarafından doğrulanarak alıcının tokenı sorunsuz bir şekilde almasını sağlar.
Merkeziyetsiz bir sistemde karşılaşılan en büyük sorunlardan biri, “çifte harcama” olarak bilinen durumdur. Bu, aynı tokenın birden fazla kez harcanması ve alıcının yanıltılması anlamına gelir. Bu sorunu önlemek için güvenilir bir mutabakat mekanizması oluşturmak gerekir.
Bu mekanizmaya Zaman Damgası Sunucusu denir. Zaman damgası sunucusu, belirli bir veri kümesini veya birden fazla işlemi bir bloğun hash değeriyle birleştirerek bir zaman damgası ile mühürler. Her yeni zaman damgası, önceki zaman damgasını referans alır ve böylece işlemlerin doğru sırayla gerçekleştiğini kanıtlar. Bu yöntem, çifte harcamayı önlemeye yardımcı olur. Ayrıca, her yeni eklenen zaman damgası, önceki tüm zaman damgalarını güçlendirdiği için geriye dönük değişiklik yapmayı zorlaştırır.
Bu sistemde, bloklardan oluşan zincir, Bitcoin madencileri tarafından üretilen hash gücü sayesinde büyür. Bitcoin ağının genişlemesiyle birlikte, çifte harcama saldırısı gerçekleştirmek için hash gücünün %51’inden fazlasını ele geçirmek neredeyse imkansız hale gelir. Bu nedenle, ağın güvenliği büyük ölçüde korunur ve çifte harcama sorununun ortaya çıkma ihtimali oldukça düşüktür.

Zaman Damgası Sunucusu
Proof of Work
İş Kanıtı (PoW), blok zinciri dünyasında en temel mutabakat mekanizmalarından biridir. Bitcoin, Ethereum ve Litecoin gibi erken dönem projeler, blok zinciri defterlerinin tutarlılığını ve değişmezliğini sağlamak için bu modeli benimsemiştir.
PoW modeli basitçe şu şekilde işler: Ağdaki tüm düğümler aynı matematik problemini çözmeye çalışır ve problemi ilk çözen düğüm, defteri güncelleme hakkı kazanır. Bunun karşılığında, blok zinciri ağı tarafından oluşturulan yeni kripto para birimiyle ödüllendirilir.
Merkeziyetsiz zaman damgası sunucusunun eşler arası işlem temelinde çalışmasını sağlamak için PoW mekanizması kullanılır. PoW’un temeli, Adam Back tarafından icat edilen Hashcash sistemine dayanır. Hashcash, başlangıçta hesaplama gücü gerektirerek gereksiz e-postaları önlemek amacıyla geliştirilmişti. Bitcoin, Hashcash’e dayalı olarak bu modeli genişletti ve blok zincirindeki işlemleri doğrulamak için madencilerin bilgi işlem gücü harcamasını gerektiren bir sistem haline getirdi.
Bitcoin’in İş Kanıtı (Proof of Work – PoW) mekanizması, hash değerinin 256 bitlik bir ikili sayı olması ve SHA-256 algoritmasıyla iki kez doğrulanması prensibine dayanır. Öncelikle, zorluk hedefi adı verilen önceden belirlenmiş bir sayı oluşturulur. Ardından, 2²⁵⁶ olası kombinasyon içinden rastgele üretilen bir hash değeri hesaplanır. Hash değerinin başında ne kadar fazla sıfır bulunursa, yani değeri ne kadar küçükse, kabul edilme olasılığı o kadar artar. Kural gereği, hesaplanan hash değeri, belirlenen zorluk hedefinden küçük olmalıdır.
En düşük hash değerini ilk hesaplayan madenci, ilgili bloğu yayınlama hakkına sahip olur. Tüm doğrulayıcılar bloğun geçerliliğini onayladıktan sonra, blok zincire eklenir ve yeni blok için madenciler tekrar yarışmaya başlar. Bu süreç, blok zincirinin sürekli büyümesini sağlar. Doğrulama, yayınlama ve muhasebe işlemleri Bitcoin protokolü tarafından otomatik olarak gerçekleştirilir. Böylece tüm düğümler (nodes), senkronize ve güncellenmiş bir deftere sahip olur.
Bitcoin ağındaki zorluk hedefi, her 2016 blokta bir otomatik olarak güncellenir ve ortalama madencilik gücüne göre ayarlanır. Hedef, her blokun yaklaşık 10 dakikada çıkarılmasını sağlayacak şekilde belirlenir. Birim zaman içinde en fazla hesaplama yapan madenci, doğru hash değerini bulma ve blok oluşturma şansını artırır. Bu mekanizma, Bitcoin’in Proof of Work konsensüs modelinin temelini oluşturur.
PoW modeli, çoğunluk gücüne dayalı karar alma süreçlerinde ortaya çıkan “çoğunluğun tiranlığı” sorununu da çözer. Ağdaki kararlar, madencilerin toplam hash gücüne dayanarak belirlenir. En uzun zincir kuralı gereği, en uzun blok zinciri geçerli kabul edilir. Eğer dürüst madenciler ağın hash gücünün büyük bir kısmını oluşturuyorsa, zincir diğerlerinden daha uzun olacak ve kötü niyetli girişimler etkisiz kalacaktır.
Bitcoin Madenciliği Nedir?
Bitcoin, blok zincirindeki işlemleri doğrulamak ve ağın güvenliğini sağlamak için İş Kanıtı (PoW) mekanizmasını kullanır. Bitcoin madenciliği ise bu sürecin sürdürülebilmesi için işlem doğrulama ve hesaplama gücü gerektiren donanımların kullanılmasıdır. Madenciler, blok zincirine yeni işlemler ekleyerek ağın senkronizasyonunu sağlar ve bunun karşılığında Bitcoin ödülü alırlar. Dünyanın dört bir yanına yayılmış olan madenciler, merkezi bir otoriteye bağlı olmadan ağın güvenliğini birlikte sağlar.
Bitcoin madenciliği genellikle altın madenciliğiyle kıyaslanır, ancak temel fark, Bitcoin madenciliğinin yeni Bitcoin’leri dolaşıma sokan geçici bir mekanizma olması ve aynı zamanda ağı güvence altına almak için madencilere teşvik sağlamasıdır.
Madenciler daha fazla hesaplama hakkı (daha fazla cevap bulmak) ve Bitcoin (blok ödülleri) elde etmek için daha fazla hesaplama gücü elde etmeye çalışır. İlk olarak, en küçük hash değerini hesaplayan madenci, ilgili bloğu yayınlama hakkı kazanır ve ardından yeni bir blok için yarış başlar. Bu süreç, madencilerin saniyede milyarlarca İş Kanıtı hesaplaması gerektiren donanımları kullanarak en son işlemleri doğrulamasıyla gerçekleşir.
Madenciler, işlem doğrulama sürecini hızlandırarak işlem ücretleri kazanabilir ve belirli bir formüle dayalı olarak yeni Bitcoin’lerle ödüllendirilir. Ancak madencilik kar getiren bir faaliyet olduğu için daha fazla madencinin ağa katılması, zorluk seviyesinin artmasına neden olur. Bu zorluk seviyesi, Bitcoin ağındaki toplam hash gücüne bağlı olarak her yaklaşık 10 dakikada bir ayarlanır.
PoW mekanizması, blokların kronolojik sırayla eklenmesini sağlar ve herhangi bir bloğu değiştirmek veya geri almak neredeyse imkansız hale gelir. Çünkü bir bloğu değiştirmek için ondan sonra gelen tüm blokları da yeniden hesaplamak gerekir. Eğer bir madenci aynı anda iki farklı blok alırsa, en uzun zincire ait olmayan blok geçersiz sayılır ve ağdaki tüm düğümler, en uzun zinciri takip ederek senkronizasyonu korur.
CPU, GPU ve ASIC Madenciliği
Madencilik teknolojisi, zaman içinde Merkezi İşlem Birimi (CPU) ile başlayan sürecin, Grafik İşlem Birimi (GPU) ve ardından Uygulamaya Özel Entegre Devre (ASIC) cihazlarına evrilmesiyle büyük bir değişim geçirdi.
Bitcoin’in ilk yıllarında, madencilik işlemleri CPU’larla gerçekleştiriliyordu ve ağın toplam hash gücü oldukça düşüktü. Ancak Bitcoin’in değer kazanmasıyla birlikte daha fazla madenci ağa katıldı, bu da madenciliği zorlaştırdı. 2010 yılında, puddinpop tarafından geliştirilen CUDA Miner ile GPU’lar, CPU’ların yerini almaya başladı. GPU’lar daha fazla işlem çekirdeğine sahip bir mimariye sahiptir ve özel madencilik talimatlarıyla CPU’lara kıyasla yaklaşık 100 kat daha yüksek hash gücü üretebilir.
Bu gelişmeye rağmen, GPU’lar da zaman içinde madencilik için yetersiz kalmaya başladı. 2013 yılında, bir şirket madencilik için özel olarak tasarlanmış bir donanım olan ASIC çiplerini geliştirdi. ASIC’ler, GPU madenciliğinden yaklaşık 200 kat daha hızlı çalışarak büyük bir verimlilik artışı sağladı. Bu gelişme, madencilik sektöründe köklü bir dönüşüme yol açarak ASIC çip üretimi ve madencilik endüstrisini önemli ölçüde şekillendirdi. Günümüzde Bitcoin madenciliği büyük ölçüde ASIC cihazlarıyla yapılmakta ve bireysel madencilik giderek daha az karlı hale gelmektedir.
Madencilik Çiftlikleri ve Bulut Madenciliği
Bitcoin madenciliğinde ödüllerin dağılımı rastgele ve öngörülemez olduğu için madenciler, gelirlerini artırmak ve maliyetleri düşürmek amacıyla kitlesel fonlama yöntemlerine yönelmeye başladı. Bu süreç, Bitcoin’in popülerleşmesinden kısa bir süre sonra madencilik çiftliklerinin ortaya çıkmasına yol açtı.
Madencilik çiftlikleri, büyük ölçekli madencilik operasyonlarını barındıran tesislerdir. Bu tesisler, yüksek işlem gücü gerektiren madencilik donanımlarını barındırarak elektrik maliyetlerini optimize etmeye ve verimliliği artırmaya odaklanır.
Öte yandan, bireyler kendi donanımlarını satın almak ve işletmek yerine bulut madenciliği hizmetlerinden faydalanabilir. Bulut madenciliği platformları, kullanıcıların madencilik makinelerini kiralayarak, teknik bilgiye ihtiyaç duymadan madencilik yapmalarına olanak tanır. Bu sistem, bireysel madencilerin donanım satın alma ve bakım maliyetlerinden kaçınmasını sağlarken, bulut madenciliği sağlayıcıları için de sürdürülebilir bir gelir modeli oluşturur.
Bitcoin Ağı Nasıl Çalışır?
Bitcoin ağı şu şekilde çalışır:
1. Yeni bir işlem ağdaki tüm düğümlere yayınlanır.
2. Her düğüm, aldığı yeni işlemi kendi bloğuna dahil eder.
3. Düğümler, kendi blokları üzerinde çalışarak Proof of Work hesaplamasını gerçekleştirir.
4. Bir düğüm, geçerli bir hash değeri bulduğunda, bloğunu tüm düğümlere yayınlar.
5. Tüm işlemler geçerli ise, diğer düğümler bu bloğu kabul eder.
6. Kabul edilen bloğun hash değeri, bir sonraki bloğun temelini oluşturur ve süreç devam eder.
Düğümler yalnızca en uzun zinciri takip eder. Eğer aynı anda iki farklı düğüm farklı bloklar yayınlarsa, ağdaki düğümler ilk ulaştıkları bloğu işleyerek zinciri uzatmaya devam eder ve diğer bloğu geçici olarak saklar. Ancak, bir sonraki Proof of Work tamamlandığında ve yeni bir blok bulunduğunda, zincir daha uzun hale gelir ve düğümler daha uzun olanı takip etmeye başlar.
Bu süreç, Bitcoin ağına tutarlılık kazandırır. Eğer bir düğüm, zincirin güncellenmiş halini kaçırırsa, bir sonraki bloğu aldığında eksik bloğu talep ederek ağ ile senkronizasyonunu sağlar. Böylece, Bitcoin ağı merkeziyetsiz bir şekilde işlemleri doğrulayarak güvenilir bir defter oluşturur.
Bitcoin’in Ölçeklenebilirliği
Bitcoin defterinin küresel tutarlılığını koruyabilmek için en uzun zincir kuralı benimsenmiştir. Blok zincirinin değişmezliğini güçlendiren en büyük hash gücüne sahip olduğu için yeni bir zincir oluşturmak veya mevcut zinciri değiştirmek mümkün değildir.
Düğümler en uzun zinciri uzatmak için yarışır ve ilk bloktan 2140 yılına kadar işlemleri kaydeder. En uzun zincirin oluşabilmesi için hash gücünün en az %50’sinin dürüst madenciler tarafından sağlanması gerekir. Bu açıdan bakıldığında, %51’lik bir saldırının gerçekleşmesi neredeyse imkansızdır.
Bununla birlikte, ağda önemli gecikmeler veya kesintiler yaşandığında ya da fikir birliği sağlanamayan anlaşmazlıklar ortaya çıktığında blok zinciri çatallanabilir. Çatallanma öncesinde defter tutarlıdır, ancak çatallanmadan sonra farklı muhasebe yöntemleri nedeniyle değişiklik gösterebilir.
Bitcoin’in İlk Çatallanması: BTC ve BCH
Bitcoin Core geliştirme ekibi, daha büyük blok boyutunun savunucuları ile görüş ayrılığı yaşadı. Core ekibi, imza bilgilerinin blok dışına taşınması, dolaylı ölçeklendirme sağlanması ve akışı dağıtmak için Ayrılmış Tanık (Segregated Witness – SegWit) ve Yıldırım Ağı (Lightning Network) gibi çözümleri savundu. Bu yöntem, blok boyutunu 1 MB seviyesinde tutarak ölçeklenebilirlik sorununa çözüm üretmeyi amaçlıyordu. Buna karşılık, diğer grup blok boyutunun doğrudan genişletilmesi gerektiğini savundu.
Core ekibi, blok boyutunun doğrudan artırılmasının merkeziyetsizliği zayıflatabileceğini öne sürdü. Diğer taraf ise Ayrılmış Tanık ve Yıldırım Ağı’nın etkisiz ve yeterince güvenli olmadığı görüşündeydi. Bu anlaşmazlık sonucunda iki taraf karşı karşıya geldi ve Bitcoin’in ilk büyük çatallanması gerçekleşti.
Bitcoin Cash (BCH), Ağustos 2017’de daha büyük blok boyutuna sahip bir alternatif olarak piyasaya sürüldü. İlk bloğu 478559 olarak kaydedildi ve Bitcoin’in orijinal 1 MB blok kapasite sınırını aşarak yaklaşık 1,9 MB büyüklüğündeydi. Tüm çatallanma öncesi Bitcoin sahiplerine, aynı miktarda BCH otomatik olarak tahsis edildi ve BCH’nin blok kapasite limiti 8 MB olarak belirlendi.
BCH, Satoshi Nakamoto’nun teknik incelemesinde tasarladığı elektronik nakit konseptine daha uygun bir yönelim benimseyerek gelişmeye devam etti. Öte yandan, BTC farklı çatallanmalar yaşadı ve zamanla dijital altın olarak konumlandırıldı.
BCH’nin Çatallanması: BSV’nin Ortaya Çıkışı
Kendisinin gerçek Satoshi Nakamoto olduğunu iddia eden Craig Steven Wright (CSW), teknik incelemede belirtilen talepleri karşılamak için BCH’nin blok boyutu sınırının tamamen kaldırılmasını ve temel protokolün sabitlenmesini önerdi. Bu fikir ayrılığı sonucunda Bitcoin SV (BSV), BCH’den ayrılarak farklı bir zincir olarak oluştu.
Bitcoin’in Üç Ana Çatallanması
Şu an itibarıyla, BTC, BCH ve BSV, farklı vizyonlarla gelişmeye devam eden Bitcoin’in üç ana çatallanmasıdır.
Bitcoin Halving
Bitcoin’in dört yılda bir gerçekleşen halving (yarılanma) döngüsü, arz ve talep mekanizmasına dayanır. Sınırsız arz, para biriminin değer kaybetmesine ve fiyatın düşmesine neden olabileceğinden, halving süreci Bitcoin’in değerini korumaya yardımcı olur.
Çıkış mekanizması şu iki temel kurala dayanır:
1. Bitcoin blokları yaklaşık her 10 dakikada bir oluşturulur ve her yeni blokta madencilere ödül olarak yeni Bitcoin basılır.
2. Ödül miktarı her 210.000 blokta bir kez azaltılır.
Matematiksel olarak, (210.000 × 10) / (24 × 60 × 365) ≈ 4 formülü, her 210.000 bloğun oluşturulmasının yaklaşık dört yıl sürdüğünü gösterir. Bu nedenle, Bitcoin blok ödülleri yaklaşık dört yılda bir yarıya düşecek şekilde ayarlanmıştır.
Bitcoin’in toplamda 32 halving sürecinden geçmesi ve bu döngünün yaklaşık 2140 yılına kadar sürmesi öngörülmektedir. Bu noktada, madenciler yeni Bitcoin kazanamayacak ve gelirlerini yalnızca işlem ücretlerinden elde edeceklerdir. Sonuç olarak, toplam arz 21 milyon BTC ile sınırlı kalacaktır.


https://www.bitcoinblockhalf.com/
Bitcoin Fiyatları
Bitcoin, 2009’daki piyasaya sürülmesinden bu yana yaklaşık on yıl içinde önemli fiyat dalgalanmaları yaşadı. Bu yazının yazıldığı tarihte, Bitcoin beş büyük fiyat zirvesi gördü ve zaman zaman %50’yi aşan düşüşler, yatırımcıları endişelendirse de uzun vadede yükseliş trendini sürdürdü.
Geleneksel piyasadaki iki güçlü varlık olan Nasdaq 100 Endeksi ve altınla karşılaştırıldığında, Bitcoin’in uzun vadeli fiyat artışı her ikisini de geride bıraktı. Yıllık bileşik büyüme oranı yaklaşık %200 olarak hesaplanıyor ve bu nedenle birçok kişi tarafından “sonsuz boğa piyasası” olarak değerlendiriliyor.
Bazı geleneksel yatırım kurumları, Bitcoin’i bir balon ya da dolandırıcılık olarak görüp değersiz bulurken, yatırımcılar onu bilgi çağının hazinesi ve dijital altın olarak değerlendiriyor. Piyasada Bitcoin’in fiyat eğilimi konusunda sürekli görüş ayrılıkları olsa da, karar vermeden önce fiyatın makul olup olmadığını belirlemek için farklı analiz yöntemleri ve bakış açıları kullanılabilir.
1. Temel Analiz:
Temel analiz, bir varlığın piyasa fiyatının makul olup olmadığını belirlemek için içsel değerini inceler. Bu tür bir analizde, Bitcoin ağının günlük işlem hacmi ve hash oranı, Bitcoin tutan benzersiz adreslerin sayısı, blok başına ödül miktarı, Bitcoin’i kabul eden işletmelerin sayısı ve genel ekonomik koşullar gibi çeşitli faktörler değerlendirilir. Uzun vadeli eğilimleri gözlemlemeye odaklandığı ve kısa vadeli dalgalanmalara karşı daha az hassas olduğu için özellikle uzun vadeli yatırımlar için uygundur.
2. Teknik Analiz:
Teknik analiz, geçmiş fiyat hareketlerini ve işlem verilerini inceleyerek gelecekteki eğilimleri tahmin etmeye çalışır. Bu analiz yöntemi, piyasadaki tüm bilgilerin fiyatlara yansıtıldığı varsayımına dayanır. Kullanım kolaylığı ve geniş uygulanabilirliği nedeniyle kripto para piyasasında oldukça popülerdir.
3. Duygu Analizi:
Duygu analizi, yatırımcıların bir varlığa olan ilgisini ölçmek için çeşitli göstergeler kullanır. Bitcoin fiyatı yükseldiğinde ve işlem hacmi arttığında, piyasanın geleceğe dair iyimser olduğu ve aktif olarak alım yaptığı düşünülebilir. Örneğin, “Bitcoin satın al” aramalarının artması veya Korku ve Açgözlülük Endeksi’nin yükselmesi bu tür sinyaller olarak yorumlanabilir.
Bitcoin’in fiyatı, zamanla değişen birçok faktörden etkilenir. İlk yıllardaki yüksek oynaklığın temel nedeni, yatırımcıların haberlere ve spekülasyonlara duygusal tepkileriydi. Bitcoin ana ağı 2009’un başlarında yayına girdiğinde fiyatı sıfırdı ve herhangi bir yasal ödeme aracı ya da fiziksel varlık ile değiştirilemiyordu. Bu nedenle, Bitcoin madenciliği başlangıçta karsızdı, çünkü pek çok kişi Bitcoin satın almaya istekli değildi.
2010 - 10.000 Bitcoin karşılığında 2 pizza satın aldı
Amerikalı yazılım mühendisi Laszlo Hanyecz, 22 Mayıs 2010’da Bitcoin forumu Bitcointalk’ta bir ilan yayımlayarak birkaç pizza satın almak için Bitcoin kullanmayı planladığını ve kendisi için sipariş verebilecek birine 10.000 Bitcoin ödemeye hazır olduğunu duyurdu. Bu işlem, 1 BTC \= 0.0002 pizza oranıyla kripto para ile yapılan ilk gerçek dünya alışverişi olarak kayıtlara geçti. O günden sonra 22 Mayıs, “Bitcoin Pizza Günü” olarak anılmaya başlandı.
Bu olay, Bitcoin’e olan ilgiyi artırdı ve hem borsa platformlarının hem de Bitcoin kullanıcılarının sayısının hızla yükselmesine katkıda bulundu.
Kaynak: Bitcointalk
2011 - Bitcoin ilk kez 1 doları aştı
California merkezli Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF), 2011’in başlarında Bitcoin bağışlarını kabul etmeye başladığını duyurdu. Bu gelişme, Bitcoin’in önümüzdeki altı ay boyunca önemli bir değer kazanmasına katkıda bulundu. Şubat ayında Bitcoin, ilk kez 1 doları aştı ve ardından birkaç hafta süren keskin yükselişlerle Mt. Gox borsasında 30 dolar seviyesine ulaştı.
Ancak Haziran ayında Electronic Frontier Foundation kararını değiştirdi ve Bitcoin bağışlarını kabul etmeyi durduğunu açıkladı. Yaptıkları açıklamada, Bitcoin’in değerini onaylamadıklarını ve insanları bu yeni para birimini rasyonel bir şekilde öğrenmeye çağırdıklarını belirttiler. Bu gelişme, piyasa güvenini ciddi şekilde sarsarak Bitcoin’in ilk büyük ayı piyasasına girmesine neden oldu. Sonraki altı ay içinde Bitcoin fiyatı %90’ın üzerinde değer kaybetti ve büyük bir düşüş yaşandı.
2013’ün ilk yarısı - İlk yarılanma 1.100 doları tetikledi
28 Kasım 2012, Bitcoin’in ilk halving (yarılanma) tarihiydi. Azalan arz ve Electronic Frontier Foundation’ın Bitcoin bağışlarını yeniden kabul etmesi, 2013 yılını Bitcoin tarihindeki en yüksek yatırım getirisinin sağlandığı dönem haline getirdi.
Yılın başında 13 dolar seviyesinde olan Bitcoin, yıl içinde %70’lik sert bir düşüş yaşamasına rağmen 1.100 dolarlık tarihi zirveye ulaştı. Bu fiyat, o dönemde altının ons fiyatına eşdeğerdi. Aynı zamanda Bitcoin’in piyasa değeri ilk kez 1 milyar doları aştı ve küresel ölçekte daha fazla yatırımcının ilgisini çekti.
2013 ~ 2014 - İkinci ayı piyasası ve siber saldırılar
2013’ün sonlarında FBI, çevrimiçi Bitcoin ödemeleri için en popüler online karaborsa ve darknet pazar yeri olan Silk Road’u kapattı. Kısa bir süre sonra, bir başka anonim pazar yeri olan Sheep Marketplace, 96.000 Bitcoin değerinde bir hack saldırısına uğradı.
2014 yılının Şubat ayı sonunda ise, dönemin en büyük Bitcoin borsası Mt. Gox, 850.000 Bitcoin kaybettikten sonra iflas etti. Bu olay, Bitcoin tarihindeki en büyük borsa skandallarından biri olarak kaydedildi. Art arda gelen olumsuz haberler ve yatırımcı güvenindeki ciddi sarsılma, Bitcoin’in ikinci büyük ayı piyasasına girmesine neden oldu.
2016 - İkinci yarılanma
İkinci Bitcoin yarılanması 9 Temmuz 2016’da gerçekleşti ve Bitcoin fiyatı, tüm zamanların en yüksek seviyesi olan 1.100 doları bir kez daha aşarak yükseliş trendine devam etti.
2017 yılının Nisan ayı ortasında Bitcoin fiyatı, 1 ons altının fiyatını geçti ve o dönemde piyasada yaygın olan, “1 BTC’nin asla 1 ons altından daha değerli olamayacağı” yönündeki söylentileri çürüttü. Bu gelişme, Bitcoin’in dijital altın olarak konumunu daha da güçlendirdi.
2017 - Yeni bir boğa turu başladı
Bitcoin, 2017 yılında hızla değer kazanmaya başladı ve yıl sonunda yaklaşık 20.000 dolara ulaştı.
Bu çarpıcı yükseliş, daha fazla yatırımcının ilgisini çekti. Bazıları doğrudan Bitcoin satın alırken, diğerleri madenci olarak ekipman yatırımı yapmayı tercih etti. Ancak, 2017’nin sonundan itibaren madencilik zorluğu hızla arttı. Aynı zamanda, donanım maliyetleri ve elektrik giderleri de yükseldi. Bu durum, madencilerin büyük amortisman ve yüksek elektrik faturalarını karşılayabilmek için çıkardıkları Bitcoin’leri satmalarına neden oldu.
Bu satış baskısı ve piyasada yaşanan olumsuz gelişmeler sonucunda, Kasım 2018’de Bitcoin fiyatı 3.000 dolara kadar düştü ve büyük bir düzeltme dönemi yaşandı.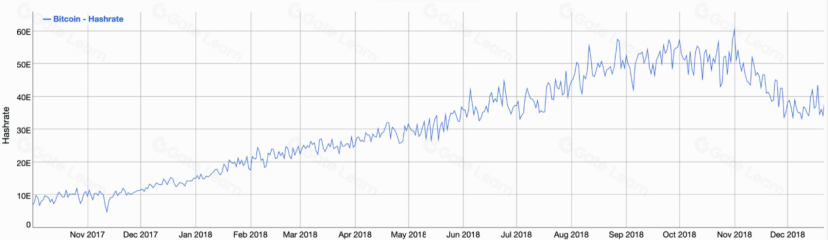
Bitcoin’in 2017’den 2018’e hash gücü, Kaynak: BitInfoCharts
2020 - COVID-19’un küresel piyasalar üzerindeki etkisi ve üçüncü yarılanma
Koronavirüs hastalığı (COVID-19), Mart 2020’den itibaren dünya ekonomilerini ciddi şekilde etkiledi. Hükümetlerin birbiri ardına serbest para politikaları uygulaması, geleneksel borsalar ve kripto para piyasasında güçlü bir yükselişe yol açtı.
Bu dönemde, Mayıs 2020’de Bitcoin üçüncü yarılanmasını yaşadı ve blok ödülleri 6,25 BTC’ye düştü. Aynı zamanda, merkeziyetsiz finans (DeFi) konseptinin hızla yükselmesiyle piyasa yeni bir anlatıya kavuştu. DeFi ekosisteminin gelişmesi, kripto piyasasına büyük bir ivme kazandırdı ve yatırımcı ilgisini artırdı.
2021 - Kurumsal fonlarla piyasa patlaması
Üçüncü Bitcoin yarılanması 18 Mayıs 2020’de gerçekleşirken, MicroStrategy, Tesla, Galaxy Digital Holdings ve Square gibi büyük kurumsal yatırımcılar Bitcoin’e yatırım yaparak piyasaya yön verdi. Kurumsal ilginin artmasıyla birlikte Bitcoin, Kasım 2021’de 68.000 dolara ulaştı ve tüm zamanların en yüksek seviyesini gördü.
Bu süreçte, giderek daha fazla insan Bitcoin’in uzun vadeli yatırım potansiyelini fark etti ve onu bir değer saklama aracı olarak görmeye başladı. Kurumsal yatırımlar, Bitcoin’in finansal piyasalardaki yerini daha da sağlamlaştırdı.
2022 - Savaş ve faiz artışıyla yeniden düşüş
2022’nin başlarında, Rusya-Ukrayna Savaşı gibi uluslararası çatışmalar, enflasyona dair artan endişeler ve Merkez Bankası’nın faiz artırım beklentileri nedeniyle sermaye, oldukça volatil olan kripto piyasasından çekilmeye başladı.
Mayıs ayında LUNA ve UST ekosisteminin çöküşü ve bunun yol açtığı kurumsal tasfiyeler, Bitcoin’in değerinde sert bir düşüşe neden oldu. Bitcoin fiyatı 17.000 dolarla en düşük seviyesine geriledi.
Piyasa değerinin büyümesi ve ticaret piyasasının olgunlaşmasıyla birlikte, Bitcoin’in fiyatı giderek geleneksel finansal piyasa ve genel ekonomik ortamla daha yakından ilişkili hale geldi ve makroekonomik faktörlere daha duyarlı olmaya başladı.
Mavi çizgi: Bitcoin, Turuncu çizgi: Nasdaq 100 Endeksi
2024 - ETF’ler, Dördüncü Halving, ABD Başkanlık Seçimleri ve Bitcoin ATH
2024 yılı, kripto para sektörü için birçok önemli gelişmeye sahne oldu. 11 Ocak 2024’te ABD Menkul Kıymetler ve Borsa Komisyonu (SEC), BlackRock, Fidelity ve Ark Invest gibi büyük firmaların spot Bitcoin ETF başvurularını onayladı. Bu ETF’ler, lansmanlarından itibaren toplamda 36 milyar dolardan fazla yatırım çekerek piyasada büyük ilgi gördü.
19 Nisan 2024’te Bitcoin ağı, dördüncü halving olayını yaşadı ve blok ödülleri 6,25 BTC’den 3,125 BTC’ye düştü. Bu olay, Bitcoin’in arzını azaltarak fiyatında yükseliş beklentisi oluşturdu.
Kasım 2024’te Donald Trump, ABD başkanlık seçimlerini kazandı. Trump, seçim kampanyası sırasında stratejik bir Bitcoin rezervi oluşturma niyetini açıkladı. Seçim zaferi, kripto para piyasasında olumlu bir hava yarattı ve Bitcoin fiyatlarında artış gözlendi.
2024’e 42 bin dolar seviyelerinde giren Bitcoin bu gelişmelerin etkisiyle 5 Aralık 2024’te ilk kez 100 bin dolar seviyesini aştı.
Bitcoin’in kısa vadeli fiyat hareketlerini tahmin etmek zordur ve sıkça farklı sektörler ile ekonomi haberlerinde tartışma konusu olur. Ancak, uzun vadeli eğilimi izlemek, belirli analiz yöntemleri ve göstergeler kullanılarak daha kolay hale getirilebilir.
Logaritmik Regresyon:
Logaritmik Regresyon, Ekim 2014’te Trolololo adlı bir Bitcointalk blog yazarı tarafından tanıtılan ilk Bitcoin fiyat tahminlerinden biridir. O dönemde Bitcoin’in fiyatı yalnızca 300 dolar seviyesindeydi. Ancak Trolololo, önceki iki fiyat rallisine ve önemli seviyelere dayanarak 2017’de 10.000 dolara, 2020’nin sonunda ise 70.000 dolara ulaşacağını cesurca öngördü.
Bu model, zaman içinde büyük ölçüde doğruluk göstermesi nedeniyle Bitcoin fiyat modelleri için bir klasik haline geldi ve sonraki tahmin modellerine temel oluşturdu.
Logaritmik regresyon, Kaynak: Bitcointalk
Stok-Akış (S2F) Modeli:
Stoktan akışa modeli (Stock-to-Flow – S2F), Bitcoin’i altın ve gümüş gibi değerli metallerle karşılaştırarak uzun vadeli fiyatın toplam dolaşımdaki arz (stok) ve yıllık üretim miktarı (akış) ile belirlendiğini öne sürer. Bitcoin’in toplam arzı sınırlı olduğundan, her yıl çıkarılan yeni Bitcoin miktarının kademeli olarak azalması fiyatın yükselmesine neden olur.
Twitter’da PlanB takma adıyla bilinen bir KOL (Key Opinion Leader), bu modeli 2019 yılında Bitcoin fiyatı 4.000 doların altındayken uyguladı ve üçüncü yarılanmanın Bitcoin fiyatını 55.000 dolara çıkaracağını tahmin etti. Bu tahminin büyük ölçüde doğru çıkması, onu kripto para topluluğunda popüler hale getirdi.
Ancak, Bitcoin’in madenciliği tamamlanıp yeni arz sıfıra yaklaştığında, stoktan akışa modeli işlevini yitirecektir. Çünkü bu durumda Bitcoin’in stoktan akış oranı sonsuz fiyat tahminleri vereceğinden modelin sürdürülebilirliği ortadan kalkacaktır.
S2F Modeli, Kaynak: Dünya Çapında Bitcoin Satın Alın
Metcalfe Yasası
Metcalfe Yasası, Bitcoin ağının değerini ve büyümesini açıklayan temel prensiplerden biridir. Bu yasa, bir ağda iletişim kurabilen N düğüm varsa, ağın değerinin N² ile orantılı olduğunu öne sürer. Yani, Bitcoin ağının değeri, kullanıcı sayısıyla doğru orantılıdır.
Bitcoin’in uzun vadeli eğilimi ve Metcalfe değeri, zincir üzerindeki aktif cüzdan adresleri, işlem sayıları ve işlem hacmi gibi faktörler incelenerek tahmin edilebilir. Bitcoin fiyatı, zincir üstü kullanıcı faaliyetleriyle doğrudan bağlantılıdır ve tarihsel verilere göre bu ilişki belirgin şekilde gözlemlenmiştir.
Sonuç olarak, Bitcoin kullanıcı sayısı artmaya devam ettikçe, Bitcoin’in uzun vadeli fiyat eğilimi de yükseliş göstermeye devam edecektir.
Bitcoin’in ağ değeri, kullanıcı sayısıyla doğru orantılıdır, Kaynak: Fidelity
Bitcoin Efsaneleri ve Gerçekleri
Kripto para birimlerinin en bilinen temsilcisi olan Bitcoin, birçok kurum ve geleneksel yatırımcı tarafından eleştirildi ve çeşitli kısıtlamalara maruz kaldı. Ancak, artan fiyatı ve giderek büyüyen popülaritesi, Bitcoin’in uzun vadeli değerini ve finansal yenilikler yaratma potansiyelini kanıtladı.
Bitcoin’in çeşitli alanlarda elde ettiği başarılara rağmen, hala birçok kişi tarafından yanlış anlaşılıyor ve bu durum, potansiyel kullanıcıların Bitcoin’i benimsemesini zorlaştırıyor. Aşağıda, Bitcoin hakkındaki bazı yaygın efsaneler ve bunların gerçek açıklamaları ele alınmaktadır.
Efsane 1: Bitcoin Anonimdir
Dışarıdan bakıldığında, Bitcoin kullanıcılarının tamamen anonim olduğu düşünülse de, gerçekte Bitcoin ağı şeffaf bir genel defter gibi çalışır. Her Bitcoin işlemi, blok zincirine kaydedilir ve herkes blockchain gezgini adı verilen araçlar aracılığıyla bu işlemleri görüntüleyebilir. Her Bitcoin, belirli bir adrese bağlıdır ve geçmişi izlenebilir.
Bir Bitcoin cüzdan adresi, rastgele harf ve sayılardan oluşan bir dizidir ve doğrudan sahibinin kimliğiyle ilişkilendirilmez. Bu nedenle, Bitcoin kullanıcılarının tamamen anonim olduğunu söylemek yerine takma ad (pseudonymous) kullandıklarını belirtmek daha doğrudur. Ancak, IP adresleri, işlem yapılan taraflar veya diğer iletişim kayıtları gibi veriler aracılığıyla kullanıcıların kimliği tespit edilebilir. Bu nedenle, Bitcoin kullanımı anonim olmaktan çok, izlenebilir bir mahremiyet seviyesine sahiptir.
Efsane 2: Bitcoin Güvenli Değil
Bitcoin ağı, milyonlarca madenci tarafından yönetilir ve açık kaynak kodu, sayısız iletişim güvenliği uzmanı ve BT araştırmacısı tarafından sürekli olarak incelenir. Blok zincirine saldırabilmek için ağın toplam hash gücünün en az %51’ini ele geçirmek gerekir ki bu, Bitcoin’in büyüklüğü göz önüne alındığında ekonomik olarak neredeyse imkansızdır.
Bitcoin, çifte harcama sorununu çözen ve “güvene dayalı olmayan” eşler arası işlemleri gerçekleştiren ilk kripto para birimi olarak öne çıkar. Bugüne kadar hiç hacklenmemiştir ve sistemin temel güvenliği korunmuştur. Ancak, Bitcoin işlemleri geri alınamaz. Yanlış yapılan transferler veya cüzdanın kaybolması durumunda, Bitcoin’ler geri alınamaz ve tamamen erişilemez hale gelir. Bu nedenle, kullanıcıların cüzdanlarını ve özel anahtarlarını güvenli bir şekilde saklamaları büyük önem taşır.
Efsane 3: Bitcoin düzenlenmiyor ve hükümetler tarafından desteklenmiyor
Bazı ülkelerin Bitcoin ve diğer kripto para birimlerinin kullanımını halen yasakladığı veya kısıtladığı doğrudur. Ancak Bitcoin’i resmi olarak tanıyan, düzenleyen ve ilgili şirketlerle bireysel yatırımcıların sıkı düzenlemelere uymasını sağlayan pek çok ülke vardır.
El Salvador ve Orta Afrika Cumhuriyeti Bitcoin’i resmi para birimi olarak kabul etmiştir. ABD, Avrupa Birliği ve birçok başka ülke ise Bitcoin’i düzenlemek için kapsamlı yasalar ve kurallar geliştirmektedir. Türkiye’de ise 2021 yılında yayımlanan yönetmelikle, kripto paraların ödeme aracı olarak kullanılması yasaklanmış ve kripto borsalarına müşterilerini tanıma zorunluluğu getirilmiştir. 2024 yılında ise Meclis’te kabul edilen yeni kripto varlık yasasıyla borsalara lisans alma şartı getirilerek yatırımcıların korunması ve piyasanın denetlenmesi amaçlanmıştır. Bu düzenlemelerle birlikte Türkiye, kripto varlık piyasasında şeffaflığı artırmayı ve yatırım ortamını güvence altına almayı hedeflemektedir.
Bitcoin’in popülerliği arttıkça, daha fazla ülkenin düzenleyici adımlar atması ve kripto para piyasasını destekleyici önlemler uygulaması beklenmektedir.
Efsane 4: Bitcoin işe yaramaz
Bitcoin şüphecileri, para birimi olarak yavaş işlem hızını eleştirmektedir. Ancak Bitcoin, insanlık tarihindeki en güvenli, şeffaf ve değişmez veri tabanlarından biridir. Kripto para dünyasında öncü olarak, blok zincirinin olanaklarını başarıyla kanıtlamıştır.
Son yıllarda düzenlemelerin iyileşmesiyle Bitcoin’in benimsenmesi de kademeli olarak arttı. Ticaret ve uzun vadeli yatırımların yanı sıra, giderek daha fazla işletme Bitcoin’i ödeme yöntemi olarak kabul ediyor. Ayrıca, borç teminatı olarak kullanılabilmesi Bitcoin’i geleneksel finans dünyasında da geçerli bir varlık haline getiriyor. Bazı kurumlar, portföylerini koruma amacıyla küçük miktarlarda Bitcoin satın almıştır.
Efsane 5: Bitcoin bir balondur
Bitcoin’in bir balon olduğunu söylemek, onu yalnızca spekülatif kazanç arayışıyla satın alanlara odaklanmak anlamına gelir ve bu bakış açısı tek taraflıdır. Bir balon, bir varlığın fiyatının gerçek değerinin çok üzerine çıkıp sürdürülemez bir şekilde yükselmesi, ardından ani bir düşüşle çökmesi durumudur.
Bitcoin, yeni bir varlık türü olduğu için gerçek değerini kesin olarak belirlemek zordur. Ancak, erken dönemlerde görülen dikey yükselişler, piyasa kapitalizasyonundaki istikrarlı büyüme sayesinde artık eskisi kadar yaygın değildir. Üstelik Bitcoin, zamanla geleneksel finans piyasalarıyla daha fazla ilişkilendirilerek halkın onun değerini daha iyi anlamasına katkıda bulunuyor.
Efsane 6: Bitcoin kara para aklama aracı olarak kullanılıyor
Massachusetts Institute of Technology tarafından yapılan bir araştırmaya göre, Bitcoin işlemlerinin yalnızca yaklaşık %3’ü suç faaliyetleriyle ilişkilendiriliyor. Chainalysis’in raporuna göre ise bu oran 2020’den itibaren %0,34’e kadar düştü. Bunun başlıca nedeni, Bitcoin’in tamamen şeffaf olması ve fon akışının kolayca izlenebilmesidir.
Birleşmiş Milletler’e göre her yıl yaklaşık 1,6 trilyon dolarlık fiat para, kara para aklama ve diğer yasa dışı faaliyetlerle bağlantılıdır. Bu rakam, küresel GSYİH’nın yaklaşık %2,7’sine denk gelir ve yasa dışı Bitcoin işlemlerinin 50 katından fazladır. Başka bir deyişle, suç amaçlı Bitcoin kullanımı hem itibari paraya kıyasla çok daha küçük bir ölçeğe sahiptir hem de zamanla azalmaktadır.
Efsane 7: Arkası olmadığı için Bitcoin’in değeri yoktur
Bitcoin’in herhangi bir varlık tarafından desteklenmemesi, değersiz olduğu anlamına gelmez. Bitcoin, enflasyonu önlemek için sınırlı bir arzla tasarlanmıştır ve madencilik sürecinde enerji ve ekipman maliyetleri harcanarak üretilir. “Çalışma kanıtı” mekanizması, bu sürecin ayrılmaz bir parçasıdır.
Fiat para birimleriyle kıyaslandığında, Bitcoin farklı bir yapıya sahiptir. 1971’de ABD’nin Bretton Woods sistemini kaldırmasının ardından, itibari para birimleri altın rezervleriyle desteklenmeyi bıraktı ve merkez bankalarının kontrolüne bağlı olarak sınırsız şekilde basılabilir hale geldi. Bu durum, bazı ülkelerde hiperenflasyona yol açtı.
Bitcoin’in değeri, fiat para birimleri gibi kullanıcı güveni ve talebe dayanır. Piyasa katılımcıları tarafından kabul edilmesi, onu değerli kılan temel faktördür. Eşler arası ödemeler, değer saklama, riskten korunma ve banka hesabı olmayanlar için finansal hizmetler gibi birçok alanda önemli başarılar elde etmiştir.
Bitcoin’in Artıları ve Eksileri
Hepimiz aynı sanat eserine bakarız ancak yorumlarımız farklı olur. Bitcoin için de tam olarak bu geçerli. Muhalifler, Bitcoin’in çevresel yıkıma neden olduğunu, sürekli spekülasyon ve aldatmacayla birçok yatırımcıyı finansal çöküşe sürüklediğini ve yüzyılın en büyük dolandırıcılığı olduğunu savunuyor. Destekçileri ise Bitcoin’in mevcut finansal sistemdeki eşitsizlik ve yolsuzluğa karşı bir çözüm sunduğunu ve insanlığa gerçek finansal özgürlük kazandıracağını düşünüyor. İşte Bitcoin’in artıları ve eksileri.
Bitcoin’in Artıları:
1. Sınırlı Arz
Bitcoin, toplam arzı 21 milyon ile sınırlı olacak şekilde tasarlanmıştır. Yeni Bitcoin üretmek için hash gücü sağlanması gerekir ve herhangi bir kişi ya da kurumun keyfi olarak Bitcoin arzını artırarak değerini düşürmesi mümkün değildir.
2. Ademi Merkeziyetçilik
Bitcoin ağı, dünya çapındaki madenciler tarafından desteklenen düğümlerle çalışır ve tamamen program kodlarıyla yönetilir. Hiçbir kişi veya kuruluşun kontrolünde değildir. Herkes bir Bitcoin düğümü çalıştırabilir ve ağın yönetimine katılabilir. Bu durum, Bitcoin’i geleneksel bankalar ve otoriteler tarafından kontrol edilen para birimlerinden ayırır.
3. Güvenlik
Bitcoin, İş Kanıtı (Proof of Work) mekanizmasını benimser ve madencilerin sağladığı hash gücü ile güvence altına alınır. Bir saldırganın ağı manipüle edebilmesi için toplam hash gücünün %51’ini kontrol etmesi gerekir ki bu, ekonomik açıdan neredeyse imkansızdır. Bugüne kadar en güvenli kripto para birimi olarak kabul edilmektedir.
4. Eşler Arası İşlemler
Bitcoin işlemleri, herhangi bir banka ya da finansal kurumun onayına gerek kalmadan doğrudan kişiler arasında gerçekleşir. Hesaplar dondurulamaz ve işlemler sansürlenemez. Bu, bireylere İnsan Hakları Evrensel Beyannamesi’nin 17. maddesinde belirtilen mülkiyet hakkını doğrudan sağlar.
5. Sınır Tanımayan Kullanım
Bitcoin, dünyanın her yerinde, her zaman, herkes tarafından kullanılabilir. Yerel düzenlemeler farklı olsa da, herkes Bitcoin’i kendi para birimine çevirebilir. Bu özelliği, Bitcoin’i küresel bir para birimi haline getirir.
6. Taşınabilirlik
Bitcoin tamamen dijital bir varlıktır ve çeşitli yollarla saklanabilir. Bir soğuk cüzdan (USB boyutunda bir cihaz), sıcak cüzdan (telefon ya da bilgisayar uygulaması) veya fiziksel bir kağıt parçası üzerindeki özel anahtar ile taşınabilir.
7. Şeffaflık ve Değişmezlik
Bitcoin işlem kayıtları blockchain üzerinde herkes tarafından görüntülenebilir ve doğrulandıktan sonra değiştirilemez. Herkes bir blockchain gezgini kullanarak işlem geçmişini kontrol edebilir, ancak kullanıcıların kimliği anonim kalır.
8. Kıtlık ve Anti-Enflasyon
Bitcoin’in toplam arzı 21 milyon ile sınırlıdır ve bu sayı kaynak kodunda sabitlenmiştir. Dört yılda bir gerçekleşen halving (yarılanma) süreci, yeni Bitcoin arzını azaltır ve 2140 yılında yeni Bitcoin üretimi tamamen duracaktır. Bu, Bitcoin’i enflasyona karşı dirençli kılar ve onu dijital altın olarak konumlandırır.
9. Uzun Vadeli Değer Artışı
Bitcoin, kripto paraların öncüsüdür ve fiyatındaki değişimler tüm piyasayı etkiler. Bitcoin piyasa değeri açısından son yıllarda büyük bir gelişim göstererek ilk 10 arasına girdi. Bu da Bitcoin’in ne kadar büyük bir değere sahip olduğunu ve kabul gördüğünü kanıtlar niteliktedir.
Kaynak: CompaniesMarketCap.com
Bitcoin’in Eksileri:
1. Yüksek Madencilik Maliyetleri
Bitcoin madencileri, ağın hash gücünü ve güvenliğini sağlamak için büyük miktarda enerji tüketmektedir. 2021 yılında toplam 138,53 terawatt-saat (TWh) elektrik harcandı, bu da 13,853 milyar kilovata eşdeğerdir. Hatta bu tüketim, bazı ülkelerin yıllık elektrik kullanımını (örneğin Arjantin ve Ukrayna) aşmıştır.
2. Çevresel Etkiler
2021 yılında Bitcoin ağı, tahmini olarak 77,27 milyon ton karbon emisyonu üretti. Ayrıca, madencilik makinelerinin amortismanı ve yenilenmesi nedeniyle yaklaşık 34.570 ton elektronik atık ortaya çıktı. Bu miktar, Hollanda’nın yıllık küçük ölçekli elektronik atık üretimine eşdeğerdir.
Kaynak: Digiconomist
3. Yüksek Oynaklık
Bitcoin, piyasa değeri açısından en büyük kripto para birimi olmasına rağmen, fiyat dalgalanmaları geleneksel finans piyasalarına kıyasla çok daha keskindir. Bu nedenle Bitcoin yatırımcıları, kısa sürede büyük değer kayıplarıyla karşı karşıya kalabilir.
4. Yavaş ve Pahalı İşlemler
Bitcoin ağı, saniyede yalnızca ortalama 7 işlem gerçekleştirebilir. Buna karşılık, Visa gibi kredi kartı ağları saniyede 2000’den fazla işlem işleyebilir. Bu durum, Bitcoin’i küresel bir ödeme ağı olarak kullanmayı zorlaştırır. Ayrıca, zincir üstü işlem ücretleri piyasaya bağlı olarak büyük değişkenlik gösterebilir ve bazı dönemlerde tek bir işlem için 60 doları aşabilmektedir.
Kaynak: YCharts
5. Geri Ödeme ve Koruma Mekanizmalarının Olmaması
Bitcoin işlemleri aracısız ve geri alınamaz şekilde gerçekleştirilir. Bu, kullanıcıların işlemlerden tamamen sorumlu olduğu anlamına gelir. Havale hataları, anlaşmazlıklar veya işlem kazaları durumunda geri ödeme yapılması imkansızdır. Daha da önemlisi, Bitcoin’i yasa dışı amaçlarla kullanan kişi veya kuruluşlara karşı hesap dondurma, ekonomik yaptırım veya kısıtlama uygulanmasını sağlayacak herhangi bir yasal mekanizma bulunmamaktadır.
6. Varlık Kaybı Riski
Bitcoin’lerin sahibi olabilmek için ilgili cüzdanın özel anahtarına sahip olmak gerekir. Özel anahtar kaybolursa, cüzdandaki tüm Bitcoin’ler de sonsuza kadar kaybedilir. Daha önce, bazı madenciler özel anahtarlarının saklandığı sabit sürücüleri kaybettikleri veya yok ettikleri için Bitcoin’lerine erişememiştir.
7. Sınırlı Kullanım Alanı
Bitcoin, değer saklama aracı ve değişim aracı olarak görülse de, yüksek oynaklığı günlük harcamalarda kullanımını zorlaştırmaktadır. Çoğu ülke ve büyük finans kurumu hala Bitcoin’i resmî olarak kabul etmemektedir. Ayrıca, Bitcoin ödemelerini destekleyen fiziksel ve çevrimiçi mağazaların sayısı oldukça sınırlıdır. Bu nedenle, kullanıcılar Bitcoin’i harcayabilmek için genellikle borsalarda yerel para birimine çevirmek zorunda kalmaktadır.
Bitcoin’in Etkisi
Bitcoin, geleneksel finans sistemine duyulan güvensizlikten doğdu. İnsanlık tarihindeki ilk kripto para birimi olarak, blockchain endüstrisine öncülük etti ve teknoloji tarihindeki diğer büyük yenilikler gibi toplum ve düşünce yapısı üzerinde derin bir etki yarattı. İşte Bitcoin ile birlikte ortaya çıkan alt kültürler, argolar, mitler ve değer değişimlerinden bazıları.
1 BTC \= 1 BTC
Bu ifade, Bitcoin’in değişmez doğasını vurgulayan bir kavramdır. Twitter’da Pierre Rochard tarafından paylaşılan ve “Bir Bitcoin, tam olarak bir Bitcoin’e eşittir” ifadesini içeren bir tabloyla popülerlik kazandı. Görünüşte anlamsız gibi duran bu matematiksel denklem, Bitcoin’in enflasyona karşı dayanıklı yapısını anlatır. Buna karşılık, ABD Merkez Bankası’nın sürekli para basması nedeniyle 1 USD, geçmişteki 1 USD ile aynı satın alma gücüne sahip değildir.
Kaynak: Elements by Visual Capitalist
HODL
HODL, bir kripto para birimini uzun vadeli olarak elde tutmayı ve fiyat dalgalanmalarına rağmen satmamayı ifade eden bir stratejidir. Terim, GameKyuubi adlı bir kullanıcının Bitcointalk forumunda Bitcoin’in düşen fiyatı karşısında çaresiz ve gergin hissettiğini, ancak yine de satmayacağını belirttiği bir yazıda ortaya çıktı. Orijinalinde HOLD yazmak isterken yanlışlıkla HODL yazdı ve bu yazım hatası hızla topluluk içinde popüler hale geldi.
Kripto para piyasasının oynak yapısı nedeniyle HODL kavramı, zamanla “Hold On For Dear Life” (Hayatın pahasına tutun) anlamında da yorumlanmaya başlandı. Böylece, yatırımcıların kısa vadeli fiyat hareketlerinden etkilenmeden kripto varlıklarını elinde tutmasını teşvik eden bir felsefeye dönüştü. Ne olursa olsun, sadece tutun!
Kaynak: Reddit
Şüpheye Düştüğünüzde Uzaklaştır
Bu ifade, komedyen Reggie Watts’ın bir röportajda hayat görüşünü anlatırken kullandığı bir sözden geliyor. Başlangıçta Bitcoin ile doğrudan bir bağlantısı yoktu, ancak zamanla Bitcoin topluluğu tarafından benimsenerek popüler hale geldi.
Bitcoin sahipleri, bu sözü piyasaya yeni giren yatırımcılara moral vermek ve onları kısa vadeli fiyat dalgalanmalarına karşı sakin kalmaya teşvik etmek için kullanıyor. Fiyat hareketleri kafa karıştırıcı veya stresli olduğunda, büyük resme odaklanmak gerektiğini hatırlatan bir motto haline geldi.
Kaynak: https://thelittlehodler.com
Lazer Gözler
Lazer gözler, kripto topluluğunda sıkça kullanılan bir avatar sembolüdür ve özellikle Bitcoin savunucularının sosyal medya profillerinde yaygın olarak görülür. Bu ifade, Bitcoin bilgisine sahip olmanın insanlara finansal piyasalardaki kaosu ve belirsizliği görme yetisi kazandırdığı fikrini mizahi bir şekilde temsil eder.
Lazer gözler, birçok animasyon ve filmde güç ve uyanışı simgeler; genellikle kahramanların özel güçlerini keşfettiği anlarda kullanılır. Bitcoin bağlamında ise, bu sembol Bitcoin’in insanları finansal gerçeklere uyandırma potansiyeline dair bir metafor olarak kabul edilir.
Kaynak: Madeni Para Bürosu
Bitcoin, 2020-2021 boğa piyasasında büyük bir yükseliş yaşarken, fiyat artışıyla birlikte halkın ilgisi ve farkındalığı da arttı. Yapılan bir anket, 2021’de ABD nüfusunun %65’inin Noel için yatırım malları almak istediğini ortaya koydu. En popüler seçeneklerden biri kripto paralar oldu ve bu durum, Bitcoin hediye kartlarını dönemin ilginç ve popüler bir hediyesi haline getirdi.
2020 öncesinde, neredeyse tüm yatırım firmaları ve hedge fonları Bitcoin’i “yutturmaca, dolandırıcılık, balon” gibi terimlerle tanımlıyordu. Ancak son yıllarda bu bakış açısı değişmeye başladı ve giderek daha fazla kuruluş Bitcoin’e tarafsız veya hatta destekleyici bir yaklaşım sergilemeye başladı.
Goldman Sachs: Yeni Bir Varlık Sınıfı
Dünyanın en büyük 10. varlık yöneticisi olan ve 2 trilyon dolardan fazla varlığı yöneten Goldman Sachs, Bitcoin konusunda başlangıçta şüpheci bir duruş sergileyen tipik bir Wall Street firmasıydı.
2017’de, dönemin CEO’su Lloyd Blankfein, Bitcoin’in “dolandırıcılık yapmak için bir araç” olduğunu söyleyerek, bu teknolojinin başarılı olacağına inanmadığını belirtti. Mayıs 2020’de Goldman Sachs, bir sunumda Bitcoin’in “bir varlık sınıfı” veya “uygun bir yatırım” olmadığını açıkladı.
Ancak 2021 yılına gelindiğinde, banka Bitcoin’e karşı tutumunu aşamalı olarak değiştirmeye başladı. Şubat 2021’de “Bitcoin henüz yatırım yapılabilir bir varlık değil” ifadesini kullanarak daha ılımlı bir yaklaşım benimsedi. Mayıs 2021’de ise “Bitcoin artık yatırım yapılabilir bir varlık olarak kabul ediliyor” diyerek tamamen farklı bir çizgiye geçti. Aynı dönemde, “Kripto: Yeni Bir Varlık Sınıfı” adlı raporlarını yayımlayarak Bitcoin’in teknolojisi ve talebi hakkında detaylı araştırmalar sundular.
Peki, Goldman Sachs neden yön değiştirdi? Digital Assets Group Başkanı Mathew McDermott bu soruya oldukça net bir yanıt verdi: “Müşteri talebi.” Başlangıçta şüpheci olan banka, artan yatırımcı ilgisi ve piyasa dinamikleri nedeniyle Bitcoin’i giderek daha fazla benimsemek zorunda kaldı.
JP Morgan: Blockchain gerçektir
Küresel varlık yöneticileri arasında yedinci sırada yer alan ve 2,5 trilyon dolardan fazla varlığı yöneten JPMorgan Chase, Bitcoin’e karşı uzun süre sert bir duruş sergiledi. Bankanın CEO’su Jamie Dimon, 2017 yılında Bitcoin’i açıkça “sahtekarlık” olarak nitelendirdi ve çalışanlarını Bitcoin ticareti yapmamaları konusunda uyardı. Hatta “Bitcoin ticareti yapan bir çalışanım olursa onu bir saniyede kovarım” diyerek kesin bir tavır ortaya koydu. Bitcoin’in “sonunun iyi olmayacağını, hükümetlerin er ya da geç onu hedef alacağını” savundu.
Ancak JPMorgan’ın tutumu zamanla değişti. İronik bir şekilde, banka daha sonra merkeziyetsizlik ilkesine ters düştüğü için eleştirilen JPM Coin adlı blockchain tabanlı bir dijital para birimi çıkardı. Jamie Dimon, ilerleyen yıllarda Bitcoin’e sahtekarlık demekten pişman olduğunu itiraf etti ve “Blockchain gerçektir” diyerek bu teknolojinin önemini kabul etti.
Dimon’ın Bitcoin hakkındaki temel çekincesi, onun hükümetlerin kontrolü dışında büyümesi ve fiat para birimlerini tehdit etmesi durumunda devletlerin onu yasaklamak veya kısıtlamak için adımlar atabileceği düşüncesine dayanıyordu. Ancak JPMorgan, Bitcoin ve blockchain teknolojisinin giderek daha fazla benimsenmesiyle birlikte daha esnek bir yaklaşıma yönelmeye başladı.
Bridgewater Ortakları: Bitcoin müthiş bir icat
Dünyanın en büyük hedge fonu olan Bridgewater Associates’i yöneten Ray Dalio, başlangıçta Bitcoin’e karşı şüpheci bir tutum sergiliyordu. Daha önce verdiği bir röportajda, “Bitcoin’in zor transferler, oynaklık ve düzenleyici belirsizlik” gibi sorunları olduğunu belirterek, kripto para birimlerinin geniş çapta benimsenmesi için gerekli yapıya sahip olmadığını düşünüyordu.
Ancak, yalnızca iki ay sonra, 2021’in başlarında Dalio fikrini değiştirdi ve “Bitcoin’in müthiş bir icat olduğunu” söyledi. Ona göre, yaklaşık on yıldır çalışan, hem para hem de değer saklama aracı olarak hızla popülerleşen, bilgisayar programlanabilir bir sistemle yeni bir para birimi yaratmak büyük bir başarıydı.
Aynı yılın Mayıs ayında, Dalio Bitcoin’e olan ilgisini bir adım daha ileri götürdü ve “Biraz Bitcoin’im var. Şahsen ben tahvil yerine Bitcoin’i tercih ederim” diyerek Bitcoin’i geleneksel finansal araçlara kıyasla daha cazip bulduğunu açıkladı. Böylece, Bitcoin’in geleneksel finans dünyasında giderek daha fazla kabul görmesinin bir örneği haline geldi.
AllianceBernstein: Bitcoin’e yer verilmesini önerdi
Wall Street kurumlarının Bitcoin konusundaki tutumlarını değiştirmesinin tek nedeni, fiyat artışıyla gelen kar fırsatları değil. AllianceBernstein buna iyi bir örnek. Firma, Ocak 2018’de, Bitcoin’in tüm zamanların en yüksek seviyesi olan 20.000 dolar civarına ulaşmasının hemen ardından, onu bir yatırım varlığı olarak reddetti.
Ancak, Bitcoin’in fiyatı 2020’de 17.000 dolara düştüğünde, firma tutumunu değiştirdi. Bitcoin’in fiyat dalgalanmalarının önemli ölçüde azalmasının, hem bireysel hem de kurumsal yatırımcılar için onu daha cazip hale getirdiğini belirterek, %1,5 ila %10 arasında bir yatırım portföyünün parçası olarak Bitcoin’e yer verilmesini önerdi. Bunu, Bitcoin’in hem değer saklama aracı hem de değişim aracı olarak giderek daha fazla kabul görmesiyle gerekçelendirdiler.
Sonuç
Bitcoin, insan uygarlığının evriminde önemli bir kilometre taşıdır. Bankacılık sistemine erişimi olmayan bireylerin doğrudan ve aracıya ihtiyaç duymadan finansal hizmetlere ulaşmasını sağlayan merkeziyetsiz, güvenli ve eşler arası bir ödeme ağı oluşturmuştur. Sonunda, Bitcoin’in başarısı, piyasa değeri bir trilyon doları aşan kripto para ekosisteminin temelini atmıştır.
Dijital altın olarak bilinen Bitcoin, kısıtlı arzı nedeniyle değerli görülür ve çeşitli yollarla satın alınabilir. Toplam arzı 21 milyon adetle sınırlıdır, ancak alım miktarı konusunda herhangi bir sınır bulunmamaktadır. Satın alınan Bitcoin’ler borsada saklanabileceği gibi, kişisel bir soğuk cüzdana da çekilebilir.
Medya ve kamuoyu tarafından defalarca “Bitcoin’in sonu geldi” söylemleri ortaya atılsa da, Bitcoin sayısız iniş çıkış, yasaklar, manipülasyonlar ve ayı piyasalarına rağmen ayakta kalmayı başardı. Hard forklar ve düzenleyici baskılara rağmen, en büyük piyasa değerine sahip ve en güçlü fikir birliğine sahip kripto para birimi olmaya devam ediyor.
Blockchain teknolojisinin yaygınlaşmasıyla birlikte Bitcoin sahiplerinin sayısı sürekli artıyor. Hükümetler ve finansal kurumlar da Bitcoin’e karşı bakış açılarını kademeli olarak değiştirerek onu yeni bir varlık sınıfı ve finansal araç olarak değerlendirmeye başlıyor. Bitcoin’in gelecekteki fiyatı belirsiz olsa da, kripto para piyasasının büyüyüp olgunlaşmasıyla birlikte Bitcoin’in önemli bir konumda kalacağı ve blockchain devriminin öncüsü olmaya devam edeceği öngörülüyor.
Yasal Uyarı
Bu içerik, yatırım tavsiyesi niteliğinde değildir. Dijital varlık alım-satımını teşvik etmeyi amaçlamaz, yalnızca bilgilendirme amaçlıdır.
Kripto varlıklar yüksek risk içerir ve ciddi fiyat dalgalanmalarına maruz kalabilir. Yatırım kararı vermeden önce kendi finansal durumunuzu değerlendirmeli ve kararınızı bağımsız olarak vermelisiniz.
Makalede yer alan veriler ve grafikler yalnızca genel bilgilendirme amacıyla sunulmuştur. Tüm içerikler özenle hazırlanmış olsa da, olası hata veya eksikliklerden dolayı sorumluluk kabul edilmez.
Gate Akademi ekibi bu içeriği farklı dillere çevirebilir. Hiçbir çeviri makale; kopyalanamaz, çoğaltılamaz veya izinsiz dağıtılamaz.
İlgili Makaleler

Tronscan Nedir ve Nasıl Kullanılır?

Türkiye’de Kripto Paraların Yasal Serüveni